High Frequency (HF)
From Signal Identification Wiki
(Redirected from HF)
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) encompasses frequencies from 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz to 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'Ghadir' OTH Radar | 'Ghadir', is an Iranian over the horizon radar, part of Iran's Sepehr Phased Radar System. | 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 29.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Pulse | 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Iran | 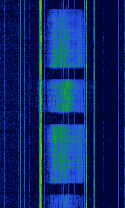 |
|
| 29B6 'Kontayner' OTH Radar | 29B6, nicknamed 'Контейнер' (Kontayner), is a Russian over the horizon radar. It is currently very active in Europe. The radar uses 150 antenna masts with data transmission systems, transmitters and receivers, a power station, and control buildings. It can detect high-altitude and low-altitude aircraft and missiles at very long ranges. | 6.1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 32 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMOP, Pulsed | 3.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 28 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 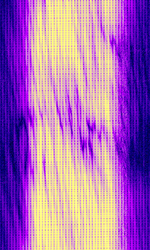 |
|
| 8PSK | 8PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol) modulation is a way to encode data using eight phase angles. Each symbol can encode three bits of data. It can achieve higher data rates than other phase modulation schemes, but it also requires a higher signal-to-noise ratio and is more prone to errors. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables),FMFrequency Modulation | 8PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol) | 125 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 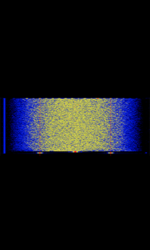 |
|
| AKKORD-SS-PD | Akkord-SS-PD (АККОРД-СС-ПД), also known as “Akkord-165” is a Russian datalink used during the invasion of Ukraine. Akkord is a rather old family of datalink protocols, Akkord-165 being the most recent version. | 7.051 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 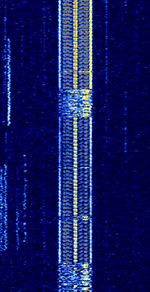 |
|
| ALE-400 | ALEAutomatic Link Establishment-400 is an amateur version of the 2G ALEAutomatic Link Establishment standard. It is adapted to the demands of amateur radio emergency traffic handling. | 1.806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.163 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 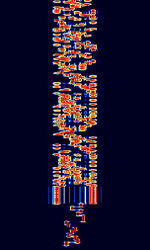 |
|
| ARQ-E(E3) | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-E, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-1000 Duplex or ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-1000D, is a synchronous full-duplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system. ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-E3 is a variant that uses a different alphabet encoding. Mainly used by French Military Forces. Stations commonly idled for hours on end. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 850 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 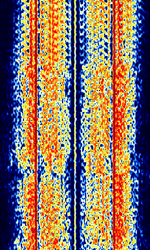 |
|
| ARQ-M2-242 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M2-242 (Also known as TDM 242, TDM-2, 96-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-28) is a two-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 242 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Marine, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 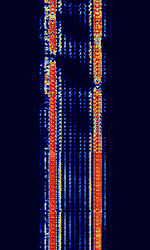 |
|
| ARQ-M2-342 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M2-342 (Also known as TDM 342, TDM-2, 96-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-28) is a two-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 342 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 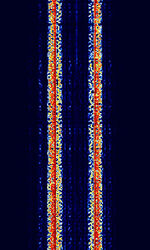 |
|
| ARQ-M4-242 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M4-242 (Also known as TDM 242, TDM-4, 192-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-56) is a four-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 242 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 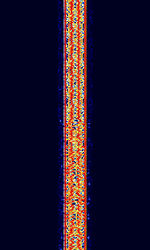 |
|
| ARQ-M4-342 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M4-342 (Also known as TDM 342, TDM-4, 192-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-56) is a four-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 342 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 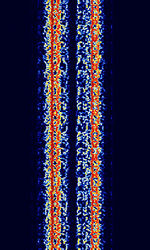 |
|
| ARQ-N | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-N is a synchronous dual channel ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query mode identical to ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-E, with the only difference being that ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-N has no symbol inversions. Formerly used by Italian Diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 850 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 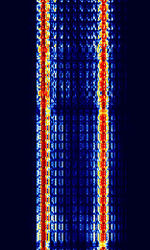 |
|
| ARQ6-90 | ARQ6-90, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-6-90 and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-6/90, is a 6-character block simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system formerly used by French and Italian diplomatic services exchange of teletype-data. It is no longer used or seen today. | 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 700 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 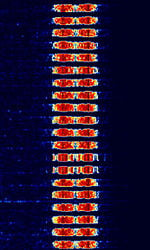 |
|
| ARQ6-98 | ARQ6-98, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-6-98 and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-6/98, is a 6-character block simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system formerly used by French and Italian diplomatic services for the exchange of teletype-data. It is no longer used or seen today. | 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| ASCII | ASCII (also known as ITA5 or IRA) is an amateur radio telegraphy signal using the ITA-5 alphabet. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation, USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 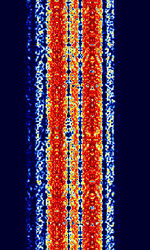 |
|
| AUTOSPEC | AUTOSPEC is a synchronous FECForward Error Correction teletype system used by British coastal stations to communicate with North Sea oil rigs. Also known as Autospec-bauer, Bauer, and Autospec Mk1. This signal is most likely phased out. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 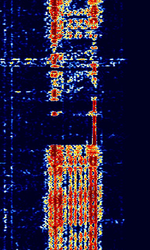 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation (AM) | Long range commercial broadcast and international radio. Also used for aviation communications. | 153 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 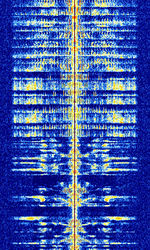 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) | Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) is a DRM-based radiotext and data technology for AMAmplitude Modulation broadcasting, like RDS that is used for FMFrequency Modulation. It transmits as a subcarrier, phase-modulating the carrier frequency. | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 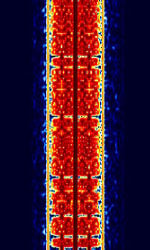 |
||
| Automatic Link Establishment (2G ALE) | Automatic Link Establishment, 2G ALEAutomatic Link Establishment (Official designation MIL-STD-188-141A and/or MIL-STD-188-141B (Appendix A)) is the current standardized method of establishing connections between radio operators. Also known as FED-STD 1045, FED-STD 1049, and STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5066. | 3.068 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.313 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 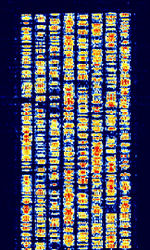 |
|
| Automatic Link Establishment (3G ALE ARCS) | 3G ALEAutomatic Link Establishment (ARCSAutomatic Radio Control System) is the next generation of ALEAutomatic Link Establishment (Designated by MIL-STD-188-141B (Appendix C)). Also known as STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4538, although MIL 188-141 does not provide Fast LSU. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 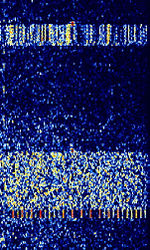 |
|
| Automatic Link Set-up (ALIS) | Automatic Link Set-up (ALIS) is an automatic link system used by Rohde & Schwarz modems. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 270 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 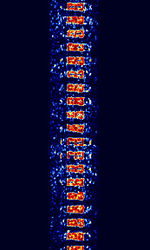 |
|
| BPM | BPM is a time signal transmitted by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, broadcasting from CAS's National Time Service Center in Pucheng County, China. | 2.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 3.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 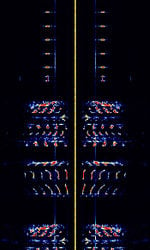 |
|
| BR-6028 | BR-6028 is a VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy (Voice Frequency Telegraph) frequency and time diversity modem using 7 data channels. It is sometimes also known as BARRIE, USA-7, or 6028. | 5.75 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15.937 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 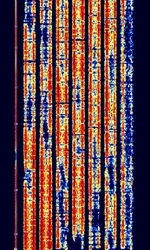 |
|
| CCIR 493-4 Selcall | CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 493-4 Selcall, also known as HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Selcall, Australian Selcall, and Codan 8580 Selcall, is a Selcall standard developed in Australia for the HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) band. Used by Amateur radio and Codan Modems. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 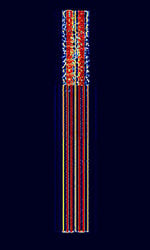 |
|
| CHIP | CHIP is a spread-spectrum PSKPhase-Shift Keying mode developed by Antonino Porcino IZ8BLY. CHIP-64 runs at 37.5 bpsBits per second (bps), whereas CHIP-128 runs at 21.09 bpsBits per second (bps). | 7.09 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.11 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 580 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 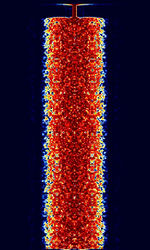 |
|
| CHU | CHU is a time signal radio station operated by the Institute for National Measurement Standards of the National Research Council of Canada. | 3.33 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.67 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 2.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Canada | 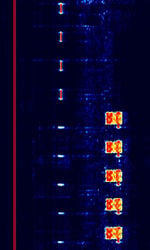 |
|
| CIS 3x100 VFT | Three CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-14 signals overlaid on top of each other in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth, operating at 100 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia |  |
|
| CIS 3x144 VFT | Three 144 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signals in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth. Reportedly phased out. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 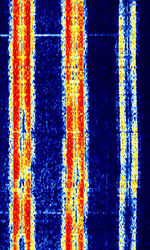 |
|
| CIS 3xBaudot-50 VFT | Three 50 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. Baudot signals in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 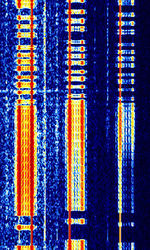 |
|
| CIS FTM-4 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic FTM-4 is the unofficial designation of a four-tone MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying data mode which is apparently used by Russian military. | 4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 13 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 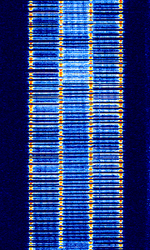 |
|
| CIS MFSK-16 XPA2 | Enigma Designation XPA2, also known as MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-16, CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-14, and CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-16, is a 14-tone MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying signal said to have origin from Russian Intelligence and Foreign Ministry stations. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia |  |
|
| CIS MFSK-16 XPB | Enigma designation XPB is a custom 16-tone MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode said to have origin from Russian Intelligence and Foreign Ministry stations. | 4.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 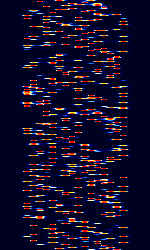 |
|
| CIS MFSK-20 XPA | Enigma Designation XPA, also known as MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-20, CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-17, and CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-20, is a 17-tone MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying signal said to have origin from Russian Intelligence and Foreign Ministry stations. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 800 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 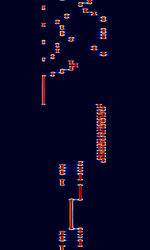 |
|
| CIS MFSK-21-13 | An MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying data mode that is believed to originate from Russian sources. Changes between MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-21, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-13 and different speeds. | 4.834 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16.292 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 3.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia, Worldwide | 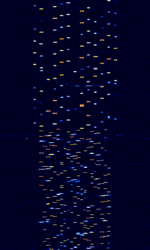 |
|
| CIS MFSK-68 | New Russian MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying Modem that uses 68 MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying (5 tones at a time) as well as a 9000 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. 8-PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol) insert every second which spans 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz wide. This signal is often found attributed with CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-3000, where CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-3000 acts as the ALEAutomatic Link Establishment for this signal as well as CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-128. It is used by Russian diplomatic services and known with the unofficial name "Perelivt". | 7.659 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18.28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 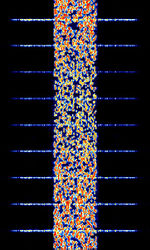 |
|
| CIS OFDM HDR Modem | Russian OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing HDR (High Data Rate) Modem. Has three main modes: CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-45, CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-60, and CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-93, corresponding to the number of OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing tones in the signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 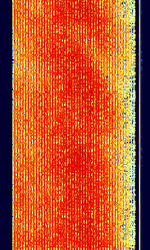 |
|
| CIS OFDM-121 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing-121 is an OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing mode that uses OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing bursts with 121 channels, spaced by two QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol)-like bursts. Not all of the 121 available channels of OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing bursts are used and it's possible to note a different arrangement of the channels in different days. | 4.454 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20.866 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 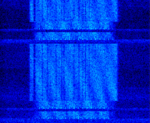 |
|
| CIS W-MFSK-17 | Presumably Russian MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying signal with wide bandwidth and 17 tones | 5.071 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 13.373 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 37.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 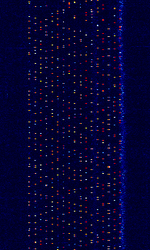 |
|
| CIS-11 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-11 (Also known as TORG-11) is a radio duplex teleprinter system used by Russian meteorological stations | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 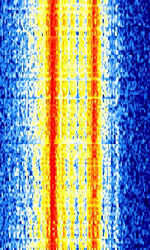 |
|
| CIS-112 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-112 OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing signal. Has a preamble of 7 Tones (not including carrier), then 56 tones before entering into the 112 tone data transmission. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 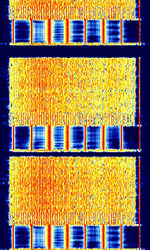 |
|
| CIS-12 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-12 (Also known as MS5, FIRE, AT-3004D, AT-3104D, T-230) is a 12-tone PSKPhase-Shift Keying Russian military multi-channel modem. | 300 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 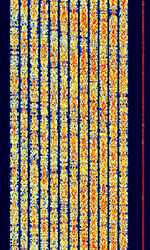 |
|
| CIS-1200 (T-230-1A 'Mahovik') | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-1200, Mahovik, "Flywheel" in Russian, is a PSKPhase-Shift Keying based mode that can transmit both voice and data. It is transmitted from a Russian T-230-1A. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | SDPSK, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 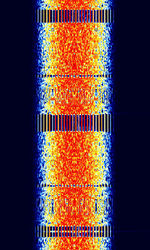 |
|
| CIS-128 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-128 is an OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing mode that uses 128 channels, with one “off” channel in the center, so the signal is divided into two 64 channel parts. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 6.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 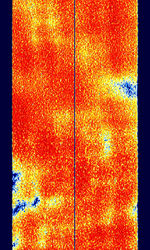 |
|
| CIS-1280 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-1280 is a OQPSK (Offset Quadrature Phase Shift-Keying) modulation data modem signal. Also known as Soviet Mil(MOD)/FAPSIFederal Agency of Government Communications and Information (Russian Agency)/PTTPush To TalkPress to TransmitMinistries of Postal, Telephone, and Telegraph Service (Soviet Agency) system. These stations are recognizable in that they are all placed on .081 offsets from a kilohertz or half kilohertz point. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 13.369 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.28 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 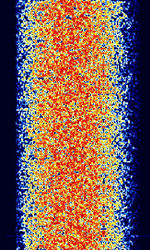 |
|
| CIS-14 | Also known as AMOR and AMOR96. Synchronous FSKFrequency-Shift Keying duplex teleprinter system with ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 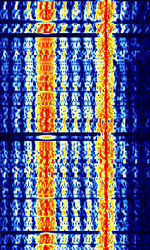 |
|
| CIS-16 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-16 is a BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) 16-tone mode, possibly transmitted from a modified AT-3004D or AT-3104 type Russian military transceiver. Also known as CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic 16x75 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. for the 75 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. speed in each of the 16 sub channels. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 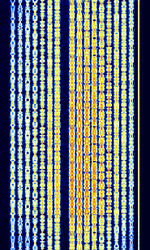 |
|
| CIS-20 | Russian AT-3104 Modem signal, 20-tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing DQPSKDifferential Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying signal. Has characteristic pilot tone located 3300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). from suppressed carrier. All 20 channels operate at 75 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 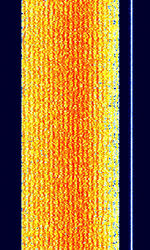 |
|
| CIS-300 | Known as CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-300 Burst, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode used with 300 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. rate with a starting and ending tone on the upper part of the signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 370 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 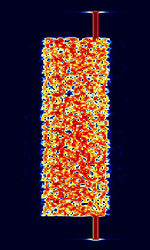 |
|
| CIS-3000 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-3000 is an 8-PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol) Data Modem protocol. Its source is traced to Russia. 3000 is for its 3000 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. speed (maximum speed is technically 9000 bpsBits per second (bps)). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 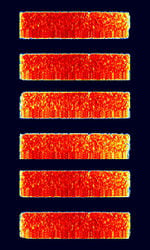 |
|
| CIS-36-50 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-36-50, also known as BEE-36, is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying modem used by the Russian Navy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 550 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 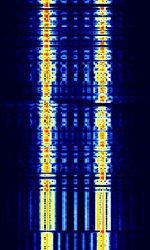 |
|
| CIS-40.5 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-40.5 (Also known as T-206) is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal used in Russian Military Communications Equipment. Used as a telegraph channel, encrypted. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 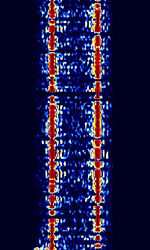 |
|
| CIS-48 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-48 is an interesting data mode with a unique format. It uses a 4 DBPSK Preamble with a constant tone and changing OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing modes as it transmits data. Origin is suspected to be in Russia. | 5.017 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 17.289 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Russia | 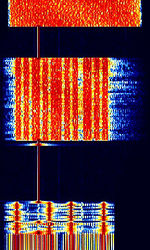 |
|
| CIS-50-50 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-50-50 is very similar to CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-36-50. The main difference is in the available baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. rates and frequency shifts used. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 150 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 630 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 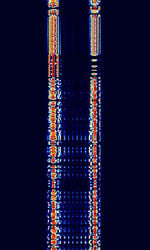 |
|
| CIS-8181 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-8181 is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying modem used by the Russian navy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 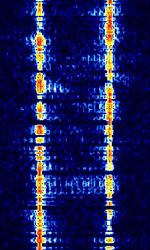 |
|
| CLOVER 2000 | CLOVER 2000 is an upgrade to CLOVER-II, a digital data protocol developed by Ray Petit and HAL Communications. Sometimes referred to as XCLOVER or 8 Tone CLOVER. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| CLOVER 2500 | CLOVER 2500 is a new upgrade to CLOVER-2000, adding 25% more speed to the CLOVER system. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| CLOVER-I | CLOVER-I was the first iteration of the Clover series of digital modes. Was never released for commercial use, replaced by CLOVER-II. Also known as Cloverleaf. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 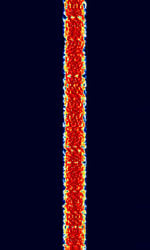 |
|
| CLOVER-II | CLOVER-II is the advancement of CLOVER-I, with 4 tone pulses and a max data rate of 750 bpsBits per second (bps). Also known as Q-CLOVER and QUAD-CLOVER. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| CODAR | CODAR (Coastal Ocean Dynamics Applications Radar) is used for near-surface ocean monitoring, such as waves and water current. | 4.438 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 42.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | ILFM | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 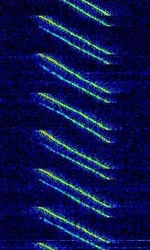 |
|
| CRY2001 Voice Scrambler | CRY2001 is a voice scrambling mode used on Sailor CRY2001 Scramblers. Fisherman often use these modes to communicate with privacy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 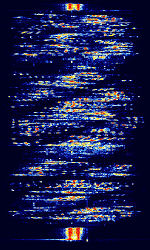 |
|
| CV-786 | CV-786 is a wideband FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode built in Rockwell-Collins MDM-2001 modems. Also known as TRC-75, as it was used in TRC-75 transceivers. A military-based Radio TeleTYpe mode. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 900 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 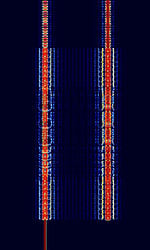 |
|
| Canadian Meteor Orbit Radar (CMOR) | Canadian Meteor Orbit Radar, or CMOR, is a meteor detection radar located near Tavistock, Ontario. | 17.45 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 38.15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Pulsed | 28 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Canada | 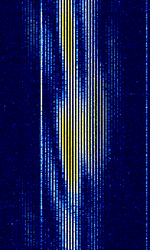 |
|
| Chinese 'Foghorn' OTH radar | A Chinese over the horizon radar, known as "foghorn" among amateur radio operators. Not much is known about it. | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 29 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China, Worldwide | 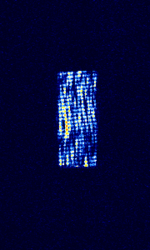 |
|
| Chinese 160kHz-wide OTH radar | Chinese OTHOver The Horizon (very long range) radar with wide bandwidth and usually low sweep rate. Little information is available. | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 29 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 160 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 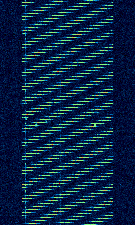 |
|
| Chinese 30-tone OFDM modem | A 30-tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing data mode, probably used by Chinese military or other agencies. | 3.618 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18.656 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | LSBLower Side Band Modulation, USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China, Worldwide | 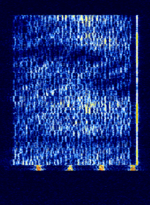 |
|
| Chinese 4+4 | Chinese 4+4, also known as 4+4 or PRC 4+4, is a multi-carrier transmission mode. It used by Chinese Diplomatic services with most traffic originating from Beijing, China. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 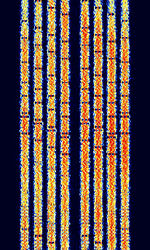 |
|
| Chinese Firedrake Jammer | Commercial AMAmplitude Modulation Broadcast jamming signal that plays Chinese folk songs to jam specific radio stations in Asia from being received by listeners. | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 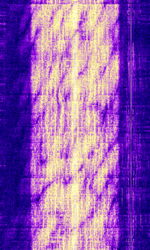 |
|
| Chinese-64 MFSK | Chinese Modem MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-64 | 3.673 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16.989 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables),LSBLower Side Band Modulation (rare) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 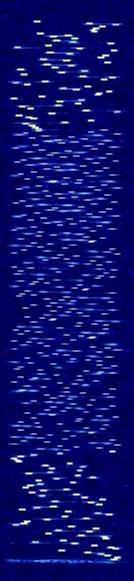 |
|
| Codan Data Modem | Codan Data Modulation for Codan Data Modems. Has 3 distinct signals: Data, ALEAutomatic Link Establishment, and SELCAL. This modulation is used in Codan's 9001, 9002, 3012 and 3212 modems. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.56 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 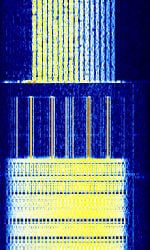 |
|
| Coherent BPSK | Coherent BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), also known as C-BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), was an experimental amateur mode developed by Bill DeCarle VE2IQ. | 138 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 18.081 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 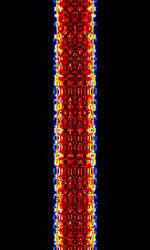 |
|
| Coherent CW | Coherent CWContinuous Wave (also known as CCW) was a strictly timed morse code mode designed by Ray Petit W7GHM (The same inventor of CLOVER). CCW depended on accurate timing from both receiver and transmitter. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Contestia | Contestia, developed by Nick Fedoseev (UT2UZ) in 2005, is a digital mode derived from Olivia. It aims to deliver a compromise of speed and performance. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 150 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 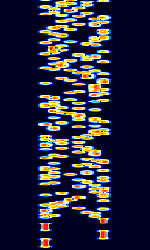 |
|
| Coquelet | Coquelet is an MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying system, similar to Piccolo. Also known as COQ-8, COQ-12, and COQUELET 8 V 2. Uses ITA-2 charset. It's two main modes are Coquelet-8 and Coquelet-13. No longer in use. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 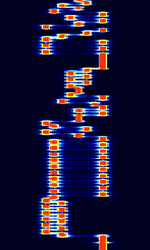 |
|
| Cuban Jammer | Cuban jammers jam the frequencies of Radio Martí, Radio Republica and occasionally WRMI radio. | 5.98 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 13.82 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | DSBDual Side Band Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Cuba | 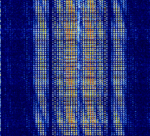 |
||
| DB0UPB research beacon | The is a research beacon for training neural networks. | 3.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.101 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | LSBLower Side Band Modulation, USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, LSBLower Side Band Modulation, USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Germany | 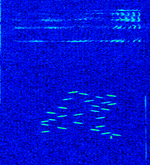 |
|
| DUP-ARQ | DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as ARTRAC and 125-ARTRAC, is a semi-duplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system once used by Thai and Hungarian Diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 325 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| DUP-ARQ-2 | DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-2 (also known as ARTRAC II) is a further development of the DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system and the system characteristics are very similar. DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-2 allows transmission of ITA-2 (Baudot) or ITA-5 (ASCII) characters depending on the application. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| DUP-FEC-2 | DUP-FECForward Error Correction-2 is a further development of the DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system and the system characteristics are very similar. Uses FECForward Error Correction instead of ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query and runs at either 125 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. or 250 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Datawell Buoy HF Link | Datawell Buoy HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Links transmitted by Datawell Marine measurement buoys, measuring ocean conditions, temperature, and wave current. | 25.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 45 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 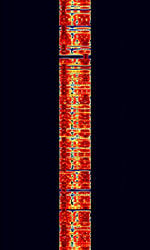 |
|
| Digisonde | Digisondes are ionosondes that use pulsed signal that can gather more radar information than a traditional ionosonde sweep. | 500 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | Pulsed | 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 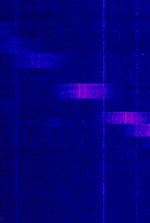 |
|
| Digital NBTV | Method for transmitting digital images via radio, similar to WinDRM or KG-STV | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) | Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) is a digital commercial broadcasting mode used to deliver FMFrequency Modulation-comparable sound quality to shortwave radio. | 531 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 26.06 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 4.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 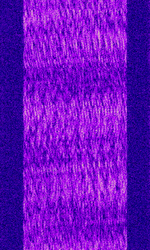 |
|
| DominoEX | DominoEX, also known as just Domino, is an IFKIncremental Frequency Keying (Incremental Frequency Keying) mode developed by Murray Greenman ZL1BPU and Con Wassilieff ZL2AFP in 2004 that was the first fully developed iteration of the Domino IFKIncremental Frequency Keying family modes. Used to send text over RFRadio Frequency. | 5.332 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.117 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IFKIncremental Frequency Keying | 173 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 524 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| DominoF | DominoF was the first experimental implementation of the Domino family of IFKIncremental Frequency Keying modes, developed by Con ZL2AFP. DominoF used dual interleaved tone sets. Superseded by DominoEX. | 1.838 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.08 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IFKIncremental Frequency Keying | 220 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Driftnet Buoy Radio Beacon | Driftnet Radio Buoys are extensively used by fishing boats operating in open seas and oceans for collecting long fishing lines or fishing nets, with the assistance of a radio direction finder | 1.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 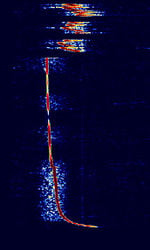 |
|
| EasyPal Digital SSTV | Seen it on the Web-SDR Twente. It could be on any frequency.
It's quite a short signal to contain a picture. Text (a callsign?) is visible in the waterfall sometimes at the end and sometimes at the beginning of the sound burst. In the audio file it is at the beginning. The signal begins at 30 second mark. Someone suggested it was Easypal made signal |
3.735 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | LSBLower Side Band Modulation | 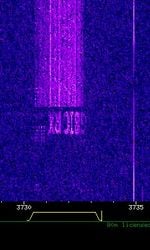 |
||||
| Ethernet Over Powerline | Ethernet Over Powerline, is an alternative way to reach ethernet cables through a set of adapters that go into outlets that can be plugged directly in the router instead of routing cables all the way from one end of a building to another. It creates the Pulse-Amplitude modulation that ethernet uses, over the RFRadio Frequency waves, and can reach a bandwidth of 60 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz depending on certain conditions. It can cause enormous interference in HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) and lower VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz). | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 60 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | PAMPulse Amplitude Modulation | 60 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 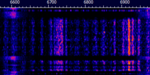 |
|
| Eurobalise downlink | Downlink from train to balise. A Eurobalise is a specific variant of a balise, a transponder placed between the rails of a railway. | 27.095 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Europe | 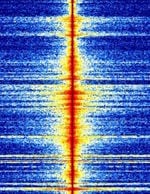 |
|||
| F03 numbers station | Enigma designation F03 is a family of digital FSKFrequency-Shift Keying modes, used by the "Polish 11" numbers station operator, which is likely a Polish intelligence agency. | 4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 21 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 800 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide, Poland | 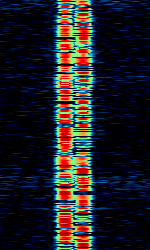 |
|
| F07 number station | F07 is a Russian digital number station known for using multiple modulation types, including MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) and FSKFrequency-Shift Keying. | 5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 17.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 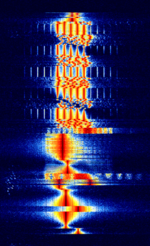 |
|
| FEC-A | FECForward Error Correction-A, also known as FECForward Error Correction-100 or FECForward Error Correction-100A, is a synchronous simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system that uses the ITA 2 alphabet. This mode was once used by many embassies, diplomatic services, and news agencies worldwide. This mode was developed by Siemens. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 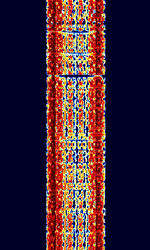 |
|
| FM NBTV | FMFrequency Modulation NBTV is a method to send moving images in a very narrow bandwidth (maximum 3 KHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz) | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 2.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 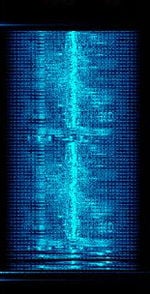 |
|
| FSQ | Fast Simple QSO (FSQ) is an amateur radio digital modulation mode developed by Con Wassilieff ZL2AFP with Murray Greenman ZL1BPU in 2015. | 3.58 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 10.149 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IFK+Offset Incremental Frequency Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 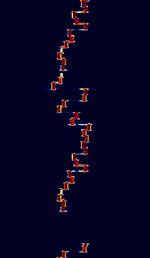 |
|
| FT4 | FT4 is an amateur radio contesting communication protocol developed by Joe Taylor (K1JT) and Steve Franke (K9AN) descended from FT8. | 10.14 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 144.17 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 83 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 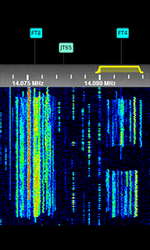 |
|
| FT8 | FT8 is an extremely-weak-signal amateur radio mode that transmits very limited communications. JS8, a variant of FT8, can send full conversations and relay messages | 1.84 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 8-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 50 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 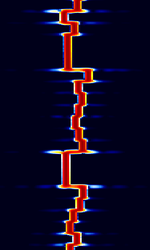 |
|
| FreeDV COHPSK | FreeDV Coherent PSKPhase-Shift Keying (Also known as FreeDV 700) is a robust Digital Voice mode developed by David Rowe for his FreeDV Digital Voice Software. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), DQPSKDifferential Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 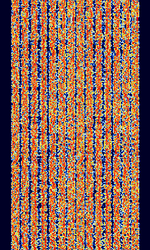 |
|
| Frequency Division Multiplex Digital Voice (FDMDV) | Frequency Division Multiplex Digital Voice (FDMDV), also known as FDMDV 14+1-tone, is a digital voice mode originally developed by Peter Martinez G3PLX and Francesca Lanza HB9TLK. It has since been improved upon by David Rowe. (FreeDV COHPSK) | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.125 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 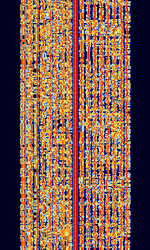 |
|
| G-TOR | Golay-Teleprinting Over Radio (G-TOR) is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying proprietary standard developed by Kantronics Inc. and is used by radio amateurs, military (Irish Air Corps/Navy, Mexican army) and governmental agencies (ICRC). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 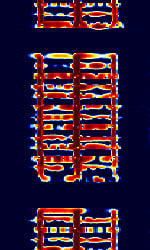 |
|
| GM2100 (R&S) | This is the proprietary HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Data Signal Protocol for the Rohde & Schwarz HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Modem GM2100. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 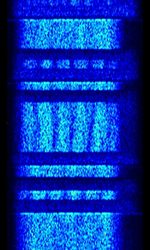 |
|
| GMDSS Digital Selective Calling | Global Maritime Distress and Safety System's Digital Selective Calling (GMDSS-DSC) is a maritime communication protocol intended to initiate ship-to-ship, ship-to-shore and shore-to-ship radiotelephone and MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz)/HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) radiotelex calls. | 2.177 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 156.525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 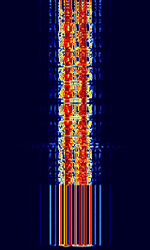 |
|
| Globe Wireless HF Network | Globe Wireless' Maritime Digital Radio was a system of 24 stations around the globe offering data services to large cargo vessels. Since 2014, GW has discontinued their HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) network. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| HC-265 Voice Scrambler | HC-265 is a Voice Scrambling mode developed by Hagelin Crypto for their HC-265 CRYPTOCOM secure voice unit. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 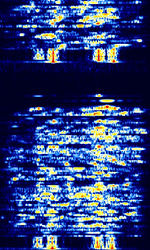 |
|
| HC-ARQ | Haegelin Crypto ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query (HC-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query) was an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying synchronous simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system used by the UN and International Rescue Committee. This mode has been phased out and is no longer in use. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 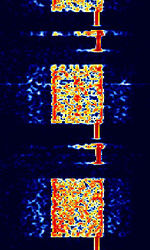 |
|
| HF trading link '120 Hz FMCW idle tone' | A HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) trading link in idle state which strongly resembles an FMCW radar with 120 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). sweep rate. Has been observed to transmit CWContinuous Wave ID once per hour. | 19.31 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20.548 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Canada / Worldwide | 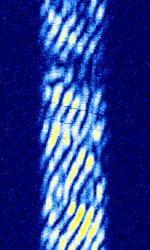 |
|
| HFGCS (High Frequency Global Communications System) | HFGCS is a series of networks deployed by the United States Air Force to send encoded messages to deployed aircraft. This network is well known for it's coded EAM's (Emergency Action Messages) used for coordinating United States Strategic Nuclear Forces. | 4.724 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15.016 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.95 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 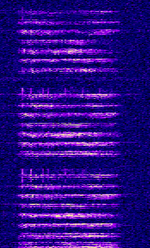 |
|
| HNG-FEC | HNG-FECForward Error Correction was a full duplex system developed and used solely by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Hungary. Used 100.05 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. with 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). shift FSKFrequency-Shift Keying. This mode is no longer used today. | 2.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 24 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Hungary | 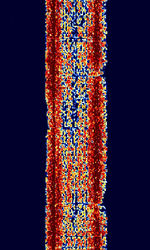 |
|
| Hellschreiber | Hellschreiber (Also known as Feld Hell or just Hell) is a teleprinter system developed in the late 1920's by Rudolf Hell, a German inventor. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 800 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 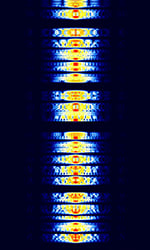 |
|
| High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program (HAARP) | HAARP is a ionospheric research program conducted in Gakona, Alaska. | 2.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation, CWContinuous Wave | CWContinuous Wave, FMCW | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
|
| High Frequency Data Link (HFDL) | HFDL, also known as HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz)-ACARS, ARINC 753, ARINC 635, and HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) DATALINK,is a data link that aircraft use to communicate short messages over long distances using HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) signals. | 2.9 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 22 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 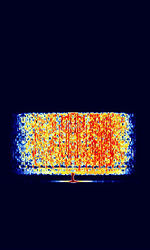 |
|
| High Frequency Data and Voice Link (HFDVL) | HFDVL (or HFD+VL) is an experimental mode developed by research groups from The University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and The Polytechnic University of Madrid. This mode is intended for military use in accordance with STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5066 parameters. | 14.35 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.829 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Spain | 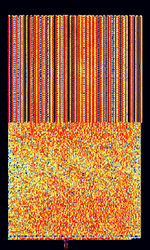 |
|
| High Power Auroral Stimulation (HIPAS) | The HIPAS (HIgh Power Auroral Stimulation) Observatory was a research facility, built to study the ionosphere and its influence on radio communications. It was located 25 miles east of Fairbanks, Alaska in the Fairbanks North Star Borough area. | 2.85 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4.53 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States | — |  |
|||
| ICAO Selcal | ICAO Selcal (also known as AVCALL, ANNEX 10, or just SELCAL) is a HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz)/VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) aviation selective calling system used by ground stations to initiate radio communications with aircraft. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 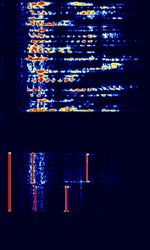 |
|
| IRA-ARQ | IRA-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as BULG-ASCII and ASCII-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, is a high data rate ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query FSKFrequency-Shift Keying system used by Bulgarian, Slovakian, and Czech diplomatic stations. The maximum speed of this mode has been seen to reach 1200 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. Not seen much much nowadays | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.35 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 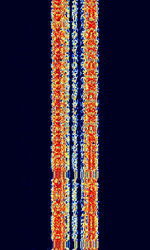 |
|
| Improved Automatic Link Set-up (ALIS-2) | ALIS-2, also known as RS-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, RS ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query 240, and MERLIN, is an improvement of the original ALIS system. ALIS-2 is used in the Rohde & Schwarz MERLIN modem. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 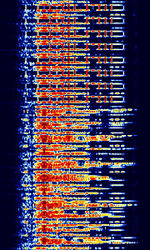 |
|
| Ionosonde | An Ionosonde (Also known as a chirpsounder or ionospheric sounder) is a radar that examines the Ionosphere and monitors HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) propagation conditions by sweeping the HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) band and receiving the echoes. | 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 40 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 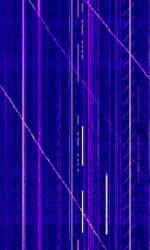 |
|
| Iranian 'Bubble' Jammer | Iranian broadcast jammer with characteristic sound. Used to suppress Radio Farda and other independent stations which broadcast to Iranian audience. | 1.547 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15.48 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Iran | 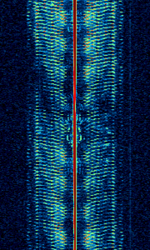 |
|
| Iranian Navy QPSK Modem | Iranian Navy QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) Modem is a QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) mode used by the Iranian Navy. It has gone through several versions. The current version (2015) is V2 and supports speeds of 468 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 936 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., and 1872 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 8.046 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 17.382 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.85 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Iran | 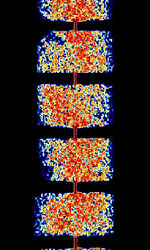 |
|
| Israeli Intelligence VFT | Israeli Intelligence based FSKFrequency-Shift Keying VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Israel | 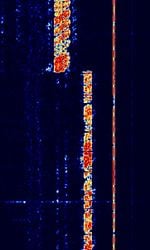 |
|
| Israeli Navy Hybrid Modem (188-110 MOD) | The Israeli Naval Hybrid Modem is based on the MIL-STD-188-110 Serial Standard. Has characteristic preamble with 4/6 Tone and 18 QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) parallel mode before 110 Serial transmission. Possible use as a broadcast transmitter for ships. Used by the Israeli Navy 4XZ station from Haifa. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Israel | 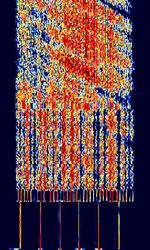 |
|
| Israeli VFT | Israeli based VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy transmission, most likely used by Israeli government or military. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Israel | 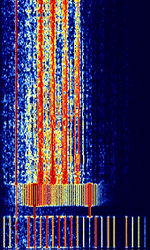 |
|
| JS8 | JS8Call is an extremely-weak-signal amateur radio communication mode based on FT8. It allows FT8 to be used for conversations and message relaying. | 1.842 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 50.318 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 50 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 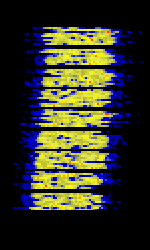 |
|
| JT4 | JT4 is a 4-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying extreme weak-signal mode which is designed especially for Earth-Moon-Earth communications. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 17 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 949 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
||
| JT65 | JT65 is an amateur radio QSO communication protocol developed by Joe Taylor, K1JT. JT65 has 3 submodes: JT65A, JT65B, and JT65C. The most popular submode of JT65 is JT65A. JT65 gets '65' from the 65 tones it uses. | 1.838 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 50.276 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 180 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 710 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 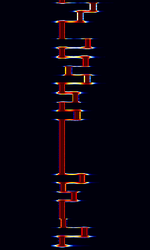 |
|
| JT9 | JT9 is a 9-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode for making contact (QSO's) under extreme weak-signal conditions. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | 3.578 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.079 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 16 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.78 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 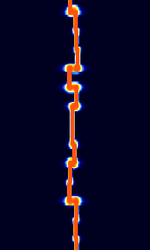 |
|
| JTMS | JTMS is a meteor scatter mode that uses MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.). JTMS behaves similarily to FSK441. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 1.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 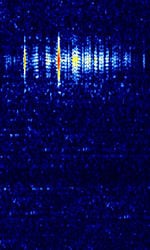 |
|
| Japan Military 8-Channel FSK | Data signal thought to originate from Japanese Military/Navy | 4.295 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16.554 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Japan | 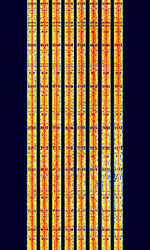 |
|
| Japanese Slot Machine (XSL) | The Japanese Slot Machine (Enigma Designation XSL) is a simplex system used by the Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force in Ichihara, Japan. | 4.153 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8.703 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Japan | 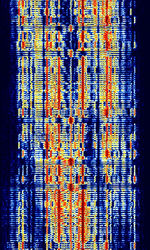 |
|
| Jindalee Operational Radar Network (JORN) | JORN is an Australian OTHR system that operates uniquely in that it's radar bursts include an intro tone before the burst. | 5.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 33 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Australia | 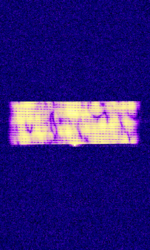 |
|
| KG-STV | KG-STV is an image transmission mode developed by JJ0OBZ in Japan. | 3.733 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 10,489.625 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying, MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 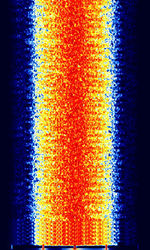 |
|
| Lentus | Lentus is an extremely slow QRPIn amateur radio, QRP operation refers to transmitting at reduced power while attempting to maximize one's effective range. mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE used to transmit QRPIn amateur radio, QRP operation refers to transmitting at reduced power while attempting to maximize one's effective range.'s at very low power. Each 43-character (75 bit) transmission takes roughly 5 minutes to transmit across 32 possible tones in a tight 25 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). bandwidth. | 136.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 14.096 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 25 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 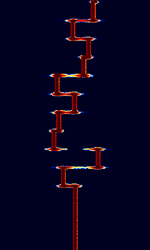 |
|
| Lightning Sferics | VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) RFRadio Frequency emissions from lightning in the atmosphere that can affect up to HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) frequencies and beyond depending on strength. Has a popping crackle sound with both USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) and AMAmplitude Modulation modes of reception. | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 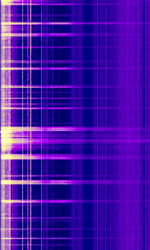 |
||||
| Link-11 | Link-11 (Also known as ALLIGATOR, STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5511, TADIL-A, MIL-STD-6011, and MIL-STD-188-203-1A) is a Tactical Data Link standard (formerly known as Tactical Digital Information Link (TADIL) used by NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization and the US Military for Maritime Tactical Data Exchange. | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 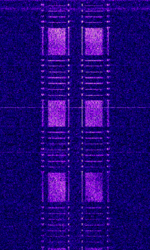 |
|
| MD-522 | MD-522 (Also known as MIL-M-55529A) is a synchronous FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode built into GRC-MD522 teletypewriter sets and used for wirelessly transmitting ASCII information. MD-522 has a narrowband, wideband, and diversity mode. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 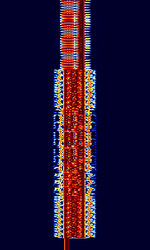 |
|
| MD-674 | MD-674, also known as Wireline FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, is a very old United States Military FSKFrequency-Shift Keying Modem from the 1960's. Uses 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). FSKFrequency-Shift Keying shift. Speeds of 50 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 75 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 100 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., and 150 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. have been logged. No longer seen today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States |  |
|
| MIL-STD-110-342 | MIL-STD-110-342 was a US Dept. of Defense standard for a 16 channel VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy teletype transmission. This mode was officially cancelled as of December 5th, 1995. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 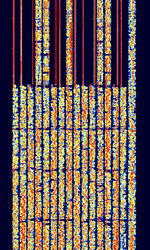 |
|
| MIL-STD-188-110 Appendix A 16-Tone | MIL-STD-188-110 Appendix A is a 16-tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing PSKPhase-Shift Keying signal used to transmit data. As of 110C revision, this mode is being phased out. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 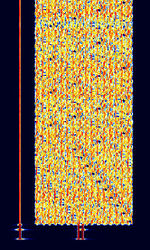 |
|
| MIL-STD-188-110 Appendix B 39-Tone | MIL-STD-188-110 Appendix B is a 39-tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing DQPSKDifferential Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying mode used to send data and voice. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 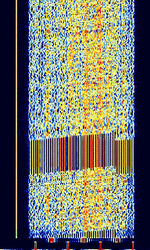 |
|
| MIL-STD-188-110 Serial | MIL-STD-188-110 Serial is a US Department of Defense standard for HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Communications, Serial PSKPhase-Shift Keying mode. Can transmit both data and voice with a range of interleaving and speed modes for optimal propagation. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 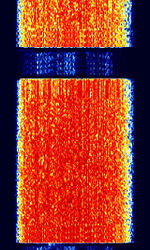 |
|
| MPDA | Experimental Multi‑Parallel Differential Amplitude Shift Keying (MP‑DASK) narrowband data mode for HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz)/VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) amateur radio text communication, created by amateur radio operator 6L5TNG in the Republic of Korea. | 1.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 53 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MP‑DASK | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| MSM-1250 Modem | MSM-1250 (Medium Speed Modem) is a 10 FSKFrequency-Shift Keying-2 OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing digital data protocol used by the stand-alone modem "SkyFax", used to transmit and receive faxes on HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 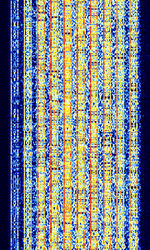 |
|
| MT63 | MT63 is a Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing) digital data mode aimed for use in high noise environments. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 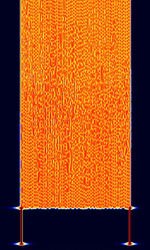 |
|
| Marconi Selenia 25-Tone Modem | The Marconi Selenia 25-Tone Modem is a military modem developed sometime around 2003 by Marconi Selenia Communications (Now Finmeccanica). It supports ECCMElectronic Counter-CounterMeasures (ECCM) is a part of electronic warfare which includes a variety of practices which attempt to reduce or eliminate the effect of electronic countermeasures (ECM) such as jamming. ECCM is also known as electronic protective measures (EPM), chiefly in Europe. capability and transmits at a datarate of 2400bps. This mode was employed by Turkey. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 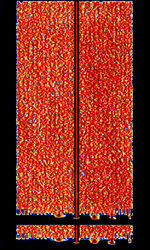 |
|
| Mazielka (X06) | Mazielka (X06) is a diplomatic selcall system used by the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Used to alert that a Serdolik transmission is going to occur soon, usually on a different frequency. | 4.963 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23.458 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 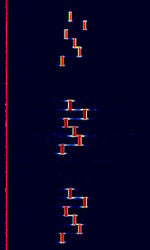 |
|
| Modernised High Frequency Communications System (MHFCS) | The Modernised High Frequency Communications System (MHFCS) is an Australian Department of Defense HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) System for their military communications network. Also known as AUS MIL ISBIndependent Side Band Modulation Modem, AUS MHFCS, and ADF HFCS. | 2.01 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 27.478 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 750 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Australia | 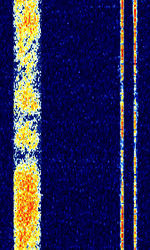 |
|
| Morse Code (CW) | CWContinuous Wave Morse Code is the simplest form of transmission found virtually all over the RFRadio Frequency bands for a variety of uses. The most common use of this is for Call-sign Beacons by both Amateur and Military operators. | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 250,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | Worldwide |  |
||
| Multi Frequency Shift Keying (MFSK) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying is a generic family of frequency shift keying digital transmission methods using more than the two tones of BFSK (binary FSKFrequency-Shift Keying). Many digital signals, especially on HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz), use MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying including WSPR, FT4 and FT8. MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-8 and MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-16 are two other well-known amateur radio modes. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 154 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 630 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Multitone Paging | Multitone Paging signal, developed by Multitone Electronics in the UK. Uses similar coding to POCSAG but the headers are different and only work with Multitone's range of paging products | 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 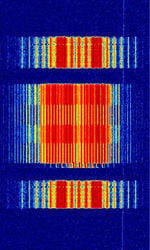 |
|
| Near Field Communication (NFC) | Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (11⁄2 in) or less. | 13.56 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying | 1.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 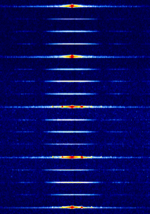 |
||
| Nokia Adaptive Message Terminal | The Nokia Adaptive Message Terminal, also known as Nokia Adaptive Burst Modem and Kryapp 302, is a Finnish encrypted messaging system suggested to be used by Finnish Intelligence Services and Swedish Military. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 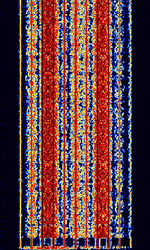 |
|
| North Korean Diplo FSK | North Korean Diplomatic FSKFrequency-Shift Keying link, teletype radio diplomatic usage. Also known as DPRK-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, KRE-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, DPRK-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, and KEGURI. Has a FECForward Error Correction stream mode and a burst ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query mode. | 9 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 29 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | North Korea |  |
|
| North Korean Diplo PSK | North Korean Diplomatic PSKPhase-Shift Keying link. Also known as KRE-PSKPhase-Shift Keying. Four speed modes have been seen, 150 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 300 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 600 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., and 1200 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. All use BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) modulation. The main identifying feature of this signal are the preambles and end of transmission patterns. | 9 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 29 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | North Korea | 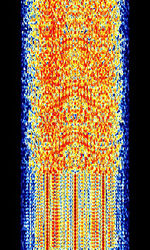 |
|
| North Korean noise jammer | Noise jammer with a carrier than tends to switch frequencies slightly lower and higher than the main signal frequency. Commonly found on 6.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | 6.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | North Korea | 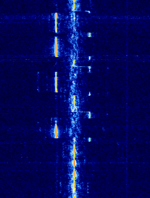 |
|
| OFDM NBTV | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing NBTV is an analog technique, in fact it is a true Fuzzy design as well. The transmission technique used is quite different from conventional TV | 3 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | Analog OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 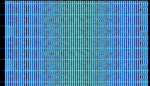 |
|
| OPERA Beacon and Data | OPERA Ad-Hoc Data/Beacon. The system is unique in that utilizes a serial data stream and Manchester coding, its therefore impossible to lose lock and its extremely robust in disturbed paths and heavy static. | 136 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 10,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 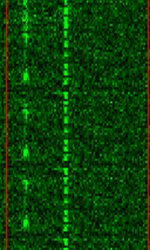 |
|
| Olivia | OLIVIA is an amateur digital teletype mode designed by Pawel Jalocha SP9VRC in 2005. Its goal was to be effective even in poor propagation conditions. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 125 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 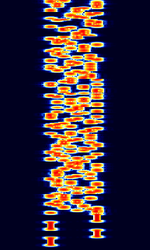 |
|
| One Beep, Two Beeps | One Beep, Two Beeps is a nickname given to a signal emitted by the Norwegian Navy communications center in Bodø | 4.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 6.429 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | Norway | 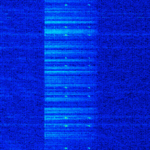 |
|||
| P03 numbers station | Enigma designation P03 is a family of digital PSKPhase-Shift Keying modes, used by the "Polish 11" numbers station operator, which is likely a Polish intelligence agency. | 4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 21 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide, Poland | 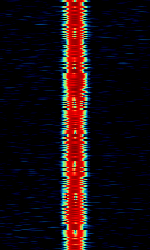 |
|
| P07 numbers station | Enigma designation P07 is a custom digital mode used by the "Russian 7" numbers station operator which is likely a major Russian intelligence agency. | 4.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 10.45 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 3.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 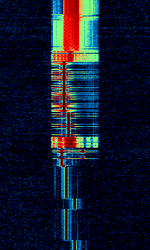 |
|
| PACKET | Packet, also known as FSK300, AFSK1200, BPSK300, QPSK600, BPSK1200, QPSK2400, AX.25 and IL2P, is a packet based protocol derived from X.25 and HDLC computer network protocols. Packet radio is a synchronous system in which data is transmitted in frames. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 730 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 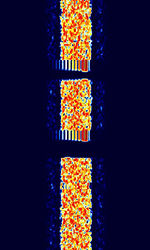 |
|
| PACTOR I | PACTOR-I is a digital data protocol combining elements of PACKET and AMTOR ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 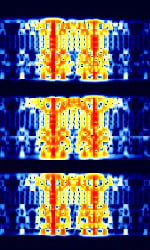 |
|
| PACTOR II | PACTOR II is an advancement of PACTOR I. It is up to 8 times faster than PACTOR I. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 450 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 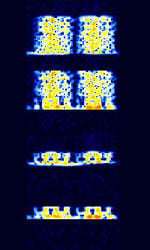 |
|
| PACTOR III | PACTOR III introduces 6 speed levels that provide higher throughput and improved robustness compared to PACTOR I and II. PACTOR III is on average 3.5 times faster than PACTOR II. With optimal conditions, PACTOR III becomes over 5 times faster. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 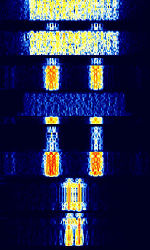 |
|
| PACTOR IV | PACTOR IV is the newest iteration of the PACTOR series, advancing from PACTOR I-III. It is 1.5x-3x faster than PACTOR III, and has 10 speed levels. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 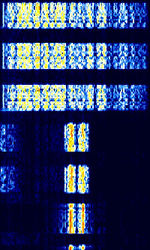 |
|
| PAX | PAX and PAX2 are developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2005, and was derived from Olivia. It utilizes the AX.25 protocol that PACKET uses, and had a minimum SNR of -10dB. Can transmit APRSAutomatic Packet Reporting System, an amateur radio-based system for real time tactical digital communications of information of immediate value in the local area frames. | 3.59 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.62 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 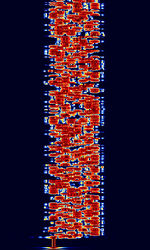 |
|
| PI4 | PI4 (PharusIgnis4) is a 4-MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode designed for amateur radio beacons. It is designed to work via different propagation modes. | 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,296 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 709 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 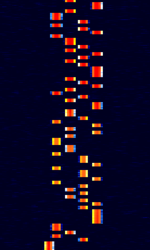 |
|
| PLUTO II OTH Radar | PLUTO II is an Over The Horizon Radar located in the Sovereign Base Area just outside RAF Akrotiri in Cyprus. PLUTO II is very active in Europe. | 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 38 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 40 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Cyprus | 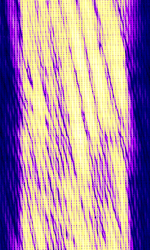 |
|
| POCSAG | POCSAG (Post Office Code Standardisation Advisory Group), also known as Super-POCSAG, Radio Paging Code No. 1 or RPC1, is a one-way 2FSK paging protocol that supports 512, 1200, and 2400 bpsBits per second (bps). | 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 932 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 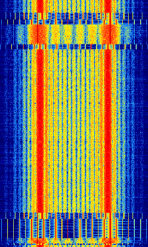 |
|
| POL-ARQ | POL-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query was a duplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system used by Polish and Italian diplomatic services. This system uses the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 476-4 alphabet with polatiry retained. No longer in use. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe | 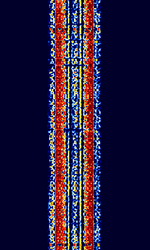 |
|
| PRC-16 | PRC-16 is a Chinese sourced PSKPhase-Shift Keying data link, traced to Shanghai. Suspected user Chinese Military. | 14.3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 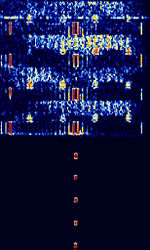 |
|
| PSK-AM | PSKPhase-Shift Keying-AMAmplitude Modulation is an amateur digital mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2002/2003, and incorporates FECForward Error Correction interleaving. PSKPhase-Shift Keying-AMAmplitude Modulation uses the modulation of PSK10/31 with the FECForward Error Correction of SITOR-B. | 10.148 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.62 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 40 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 180 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Panther-H Modem | Panther-H is an intelligent frequency hopping transceiver developed by Racal (now Thales Group). Has a signature 8-burst SOC (Start Of Conversation) sync procedure. Used in Panther-2000H radios | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 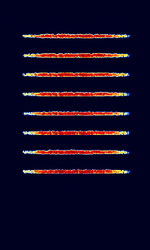 |
|
| Phase Shift Keying (PSK) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying is a digital teletype mode based on Phase-Shift Keying (PSKPhase-Shift Keying) modulation. The most popular amateur radio PSKPhase-Shift Keying mode is PSKPhase-Shift Keying 31. | 1.838 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 909 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 10 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 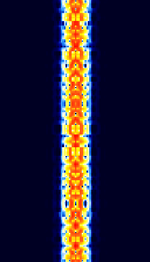 |
|
| Piccolo | Piccolo was a MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying system developed by the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO) to communicate with foreign embassies and UK military stations around the world. No longer used. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 180 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 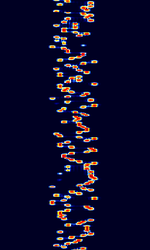 |
|
| Podsolnukh 'Sunflower' Radar | A Russian over the horizon radar, also known as "Sunflower" | 3.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis. | FMOP | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia, Worldwide |  |
|
| Polish Intelligence 100bd 625Hz FSK | Also known as F11, this is a one-way broadcast system that was used by one of Polish intelligence agencies for delivery of messages to their operatives abroad on fixed schedules. | 4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Poland | 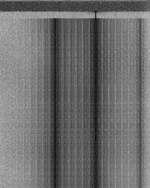 |
|
| Q-MAC HF Modem | The Q-MAC HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Modem is a military modem developed by Q-MAC (acquired by Barrett Communications). It uses OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing with a BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) sync channel in a gap of the signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, PSK8 | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 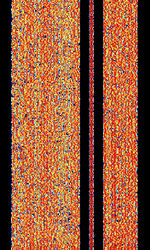 |
|
| Q15X25 | Q15X25, also known as NEWQPSK, is an experimental amateur radio packet modem developed by Pawel Jalocha SP9VRC. Q15X25 is a OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) implementation of the AX.25 Packet protocol used in PACKET. | 3.585 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.109 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.95 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.35 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 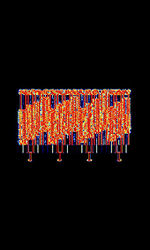 |
|
| RAC-ARQ | RAC-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as MEROD and RACAL-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, is a teleprinter system by Racal, used in MEROD devices. MEROD stands for Message Entry and Read Out Device. Hasn't been seen since 2010. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 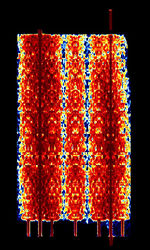 |
|
| RF heating and welding interference | Radio frequency heating and welding equipment may radiate interference which can be picked up by radio receivers. On a waterfall display, it usually appears as wobbly peaks that rapidly drift downwards in frequency. | 24 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | CWContinuous Wave, FMFrequency Modulation | Worldwide | 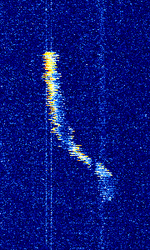 |
||
| RFID | Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. The tags contain electronically-stored information. Passive tags collect energy from a nearby RFID reader's interrogating radio waves. | 125 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 13.56 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 3.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 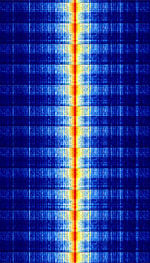 |
|
| ROS | ROS is an amateur radio teletype free running QSO mode designed for low signal/high noise conditions. | 1.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | DSSS | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| RTTYM | RTTYM, developed by Nick Fedoseev (UT2UZ) in 2005, is a digital mode derived from Olivia. It aims to deliver a compromise of speed and performance. RTTYM is about 4x faster than Olivia, but trades the speed for reduced robustness and sensitivity. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 150 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 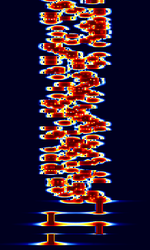 |
|
| RUM-FEC | RUM-FECForward Error Correction, also known as ROU-FECForward Error Correction and SAU-FECForward Error Correction, is a FSKFrequency-Shift Keying FECForward Error Correction system used by Romanian diplomatic services. This is no longer used today, replaced by MIL-STD 188-110 Serial. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 750 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Romania | 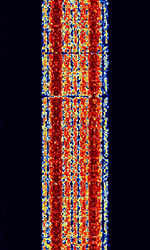 |
|
| RUM-MOI FEC | RUM-MOI FECForward Error Correction, also known as RUM-MIL 115.76 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., is a FSKFrequency-Shift Keying FECForward Error Correction mode used by the Romanian Ministry of Internal Affairs, supposedly under military use. This is no longer used today, replaced by MIL-STD 188-110 Serial. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Romania | 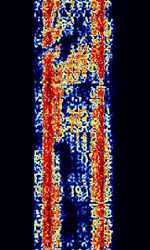 |
|
| RWM | RWM is a Russian shortwave time signal station. | 4.996 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.996 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 5 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia |  |
|
| Radio Teletype (RTTY) | RTTYRadio TeleTYpe (Also known as Baudot or ITA2) uses the Baudot 5-bit alphabet with FSKFrequency-Shift Keying to send text messages over the shortwave. This mode is gradually dying out in favor of more robust modes like PSK31 in the amateur service. | 147.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 28.15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 850 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Redundant Digital File Transfer (RDFT) | RDFT is an amateur radio digital mode used to transmit files. | 9.065 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 9.24 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 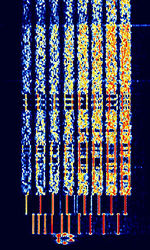 |
|
| Relocatable Over-the-Horizon Radar (ROTHR) | Relocatable Over-the-Horizon Radar (ROTHR), also known as AN/TPS-71, is an OTHOver The Horizon (very long range) Radar used by the United States Navy that uses bistatic ionospheric backscattering for wide area surveillance. | 5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 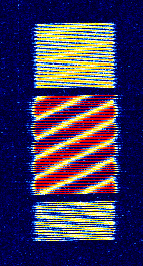 |
|
| Robust PACKET | Robust PACKET, also known as HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz)-APRSAutomatic Packet Reporting System, an amateur radio-based system for real time tactical digital communications of information of immediate value in the local area, RPR, Winlink RMS, and APRSlink, is an OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing version of the amateur mode PACKET which is optimized for shortwave use. This mode was developed by Spezielle Communications Systeme GmbH & Co. KG (SCS). | 3.61 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.103 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 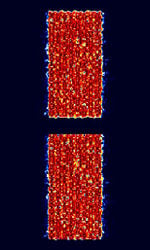 |
|
| Russian Diplo VFT PSK 64Bd | Russian Diplomatic 3 channel VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy PSKPhase-Shift Keying running at 64 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. Enigma M42 designation | 4.022 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23.131 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 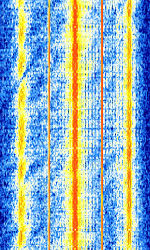 |
|
| Russian Intelligence 200bd 1000Hz FSK (F06) | Also known as F06, this is a one-way error-correcting broadcast system, used by one of Russian intelligence agencies for delivery of messages to their operatives abroad on fixed schedules. | 4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 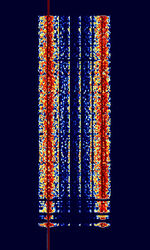 |
|
| Russian Intelligence 200bd 500Hz FSK (F01) | Also known as F01, this is a digital FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode used by Russian intelligence to deliver encrypted messages to their operatives abroad. Transmissions usually happen on fixed schedules. | 4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia |  |
|
| Russian MFSK-OFDM-chirp hybrid modem | A supposedly Russian HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) data mode with MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing and frequency sweeps, resulting in an interesting spectrogram and sound. | 12.176 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16.259 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, FMFrequency Modulation, FMCW | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 96 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia, Worldwide | 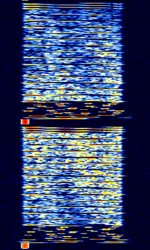 |
|
| Russian military 20bd 7kHz FSK | Slow 20-baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal with very large 7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz frequency shift. Used by Russian military. | 7.041 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 7.063 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 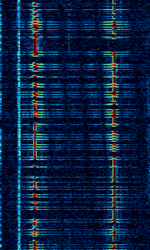 |
|
| SI-ARQ | SI-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-S and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-1000S, is a simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system designed by Siemens formerly used by Austrian and Indonesian diplomatic services. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe |  |
|
| SI-FEC | SI-FECForward Error Correction, also known as FECForward Error Correction-S, FECForward Error Correction 1000 Simplex, and FECForward Error Correction-1000S, was the FECForward Error Correction variant of SI-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, and was only used under extremely poor propagation conditions. SI-FECForward Error Correction was developed by Siemens and was used by Austrian and Indonesian diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 280 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe | 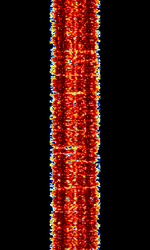 |
|
| SITOR-A | SITOR-A (Also known as AMTOR-A) is one of two modes of SITOR, which stands for Simplex Teletype Over Radio. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 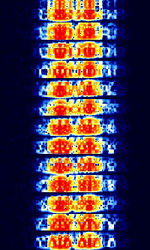 |
|
| SITOR-B | SITOR-B is one of two modes of SITOR (Simplex Teletype Over Radio). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 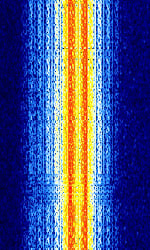 |
|
| SKiYMET meteor radar | SKiYMET is a meteor detection radar which is used by many research institutes around the world. It can use different transmission parameters and can be received over long distances during sporadic-E and other special propagation conditions. | 29 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 40 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Pulsed | 160 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 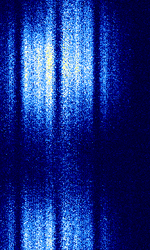 |
|
| SP-14 (XP) | SP-14 (XP) was a 14 tone MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode with origins from the Russian Intelligence and Foreign Ministry. Also known as NUM-13. Inactive since 2005, superseded by XPA. | 9 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia |  |
|
| SPREAD | SPREAD, also known as AUTOSPEC Mk2, SPREAD-11, SPREAD-21, and SPREAD-51, was a FECForward Error Correction system used by Romanian diplomatic stations and the Brazilian Navy and shore stations. SPREAD is considered the successor to AUTOSPEC. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 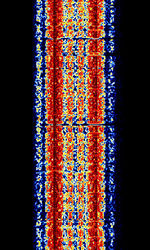 |
|
| STANAG 4197 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4197 is a NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing signal used in ANDVT modems that transmit encrypted digital voice over HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 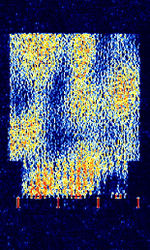 |
|
| STANAG 4285 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4285 is specified by the NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) Military Agency for Standardization in "Characteristics of 1200 / 2400 / 3600 Bits per Second Single Tone Modulators / Demodulators for HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Radio Links" | 1.89 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 22.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 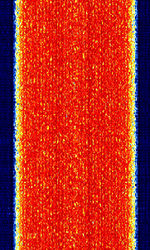 |
|
| STANAG 4415 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4415 is a NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization standard for robust, non-hopping digital data communication, used on severely degraded HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) channels with large Doppler and multipath spreads. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 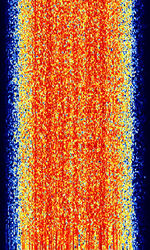 |
|
| STANAG 4481 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4481, also known as CRATT, Link-4, and NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization-75, is specified by the NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) Military Agency for Standardization as a "Minimum technical equipment standards for naval HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) shore-to-ship broadcast system" | 2.815 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18.016 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 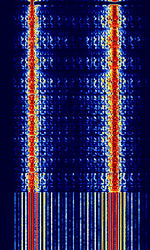 |
|
| STANAG 4529 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4529 a modification of STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4285 to deliver data and voice in 1240 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). of bandwidth at rates of up to 1800 bpsBits per second (bps). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), 8PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol) | 1.24 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 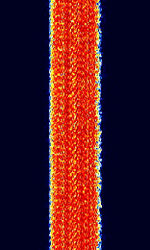 |
|
| STANAG 4539 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4539 or MIL-STD-188-110B/C Appendix C is a HDR (110B) / MDR (110C) serial PSKPhase-Shift Keying/QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation signal that can reach speeds up to 9600 bpsBits per second (bps) (12800 bpsBits per second (bps) with no interleaving). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 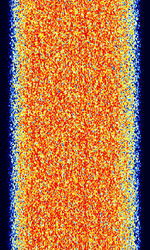 |
|
| SWED-ARQ | SWED-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-SWE, was a Swedish simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system used by Swedish diplomatic services. This protocol supported three packet lengths and was able to change packet length mid-transmission. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Sweden |  |
|
| Saab Grintek MHF-50 MFSK Modem | The MHF-50 MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying Modem by Saab Grintek Technologies in South Africa is a data modem that utilizes RTTYRadio TeleTYpe, 2-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, and 33-MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying to transmit data | 4.245 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12.982 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | South Africa |  |
|
| Serdolik | Serdolik is a MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying signal used by the Russian diplomatic service. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 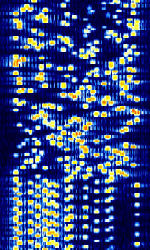 |
|
| Siemens CHX-200 FSK Modem | CHX200, also known as Siemens CHP200 and PRC-921/GY, is a backpack HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) ECCOM transceiver, designed and built by Siemens. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Single Sideband Voice | Single-sideband voice is a subtype of AMAmplitude Modulation voice modulation. It is used in HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) amateur bands and for weak signal VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) and UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) voice, as well as aircraft weather reports. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 1.9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 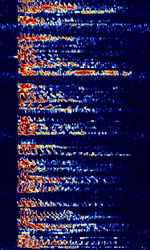 |
|
| SkyOFDM | Data transmission mode developed by SkySweep Technologies in Finland. Probably used by Finnish MFA | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Finland | 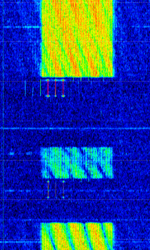 |
|
| Slow-Scan Television (SSTV) | Slow-scan television (SSTV) is a method for picture transmission used by amateur radio operators to transmit and receive images. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables), LSBLower Side Band Modulation, NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 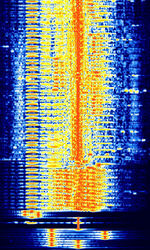 |
|
| Snap Circuits SCROV-10 Remote Control | A remote control transmission from the controller from an Elenco Snap Circuits SCROV-10 kit. | 27.145 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying | 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 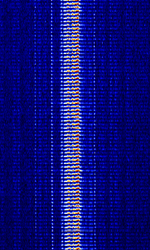 |
||
| Spectrum Painting | A form of SSTV that directly modulates an image to IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis. by scanning across it so it shows up when viewed using a waterfall. Used by Hams for experimentation methods. | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables), LSBLower Side Band Modulation | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| SuperDARN (Super Dual Auroral Radar Network) | SuperDARN (Super Dual Auroral Radar Network) is an international radar network used for scientific purposes. The network is used to study plasma convection in the upper atmosphere. | 9 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PPMPulse Position Modulation | 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 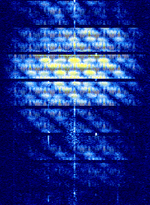 |
|
| Switching Electronic Interference | Commonly experienced interfering RFRadio Frequency emissions from switching electronics (i.e. switched-mode power supplies, power converters, digital electronics, etc.) which use inductors (coils) that unintentionally act as antennas. | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 200 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 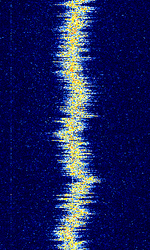 |
||||
| THOR | THOR is an adaptation of DominoEX with MFSK16 binary varicode and FECForward Error Correction. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IFKIncremental Frequency Keying | 173 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 524 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 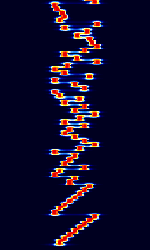 |
|
| THROB | THROB is a unique data mode that relies heavily on DSP techniques, using MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying and AMAmplitude Modulation modulation techniques together. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 72 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 188 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 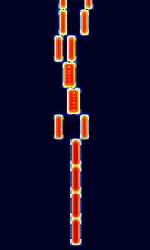 |
|
| TT2300 | TT2300, also known as TT2300B, TT2300-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, TRA-2300, and TPLEX, is an 8MFSK synchronous system developed by Thrane & Thrane of Denmark (acquired by UK defense firm Cobham in 2012). | 5.029 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 7.72 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 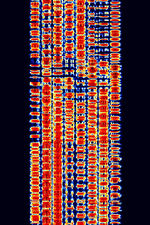 |
|
| TWINPLEX | TWINPLEX, also known as F7B4 and TWINPLEX-SITOR, was a diplex 4-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query mode developed by Mackay Radio and Telegraph Company, based in New York City, in the early 1950's. TWINPLEX was used by Interpol, the United Nations, and other diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 450 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 950 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Thales SALAMANDRE (HFXL) | Thales SALAMANDRE (using HFXL waveform) uses up to 16 separate contiguous or not-contiguous narrowband HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) channels for high datarate military and tactical communications. Operates on a modified STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).-4539 platform. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 150 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 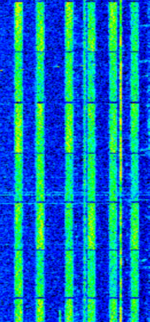 |
|
| Thales Système 3000 HF Modem | Thales Système 3000 is a HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) modem capable of many different modes of transmission. It has a unique preamble and format to it's signals. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 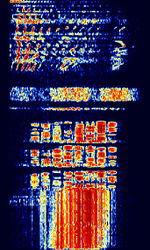 |
|
| Thales Système 3000 Skyhopper | Thales Système 3000 Skyhopper is the frequency hopping mode of the Système 3000 Modem. Characterized by it's very short bursts and frequency hopping behavior. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 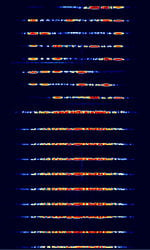 |
|
| Thales Système 3000 Voice Scrambler | Voice Scrambling mode from Thales Système 3000 HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Modem. Has characteristic PSKPhase-Shift Keying and MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying bursts at the beginning and end of a voice transmission. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| The Alarm | Channel marker of a Russian military station nicknamed "The Alarm". "The Alarm" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District. So far, apart from test counts, it has not been heard with any actual traffic. | 4.77 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 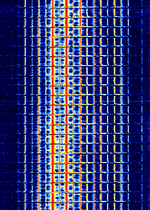 |
||
| The Goose | "The Goose" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District. It broadcasts on 4310 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz during daytime, changing to 3243 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz for nighttime. | 3.243 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4.31 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 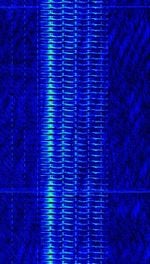 |
|
| UK GOV MIL WINDRM51 | UK GOV/MIL "WinDRM51" variant. Unknown purpose, But link between UK & Cyprus has been found some years ago. | 9.104 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 13.451 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 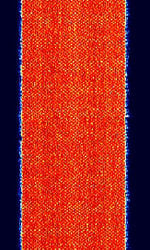 |
|
| UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) Time Standard | UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) time standard transmission from NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) stations WWV in Fort Collins, Colorado USA (2.5, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz) and WWVH in Kauai, Hawaii (2.5, 5, 10, 15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz). | 2.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 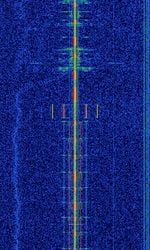 |
||
| Ultra Low Latency (ULL) Electronic Trading Network | A 48k or 24k baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. OQPSK signal that is strongly suspected (through numerous circumstantial pieces of evidence) to be either an experimental or active P2P RFRadio Frequency link between financial market data centers, used for High Frequency Trading (HFT) and other latency-sensitive market activities. | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | OQPSK | 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 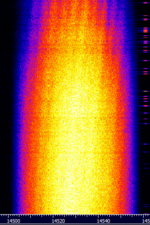 |
|
| VARA HF | VARA HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) is a sound-card mode used to exchange traffic (Mostly Winlink traffic) on the HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) bands | 1.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), 4-8PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol), 16-32QAM, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 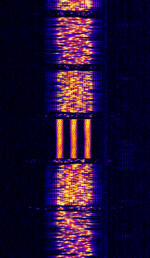 |
|
| VEZHA-S | Two-way 100 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second./500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). Russian Telegraph system, attributed name VEZHA-C (Tower-S), usage claimed to be by Russian Ministry of Communications (MinComSvyaz Rossii). Possible usage in meteorology under callsign RWD59. | 2.755 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12.165 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 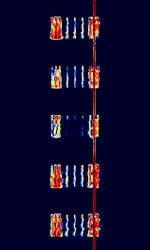 |
|
| VISEL | VISEL, also known as YUG-MIL 120.9 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., FECForward Error Correction-12, and YUG-MIL FECForward Error Correction, is a synchronous teleprinter system used by the former Yugoslav military. No longer active today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe | 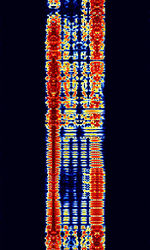 |
|
| VOICE | VOICE is a MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2006, and was derived from Olivia. It was designed for blind or partially sighted amateur radio operators. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 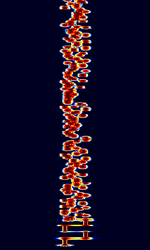 |
|
| Vietnamese Siren Jammer | Used to interrupt AMAmplitude Modulation boardcast stations such as Radio Free Asia, Radio Đáp Lời Song Núi as well as Radio Sweden. | 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 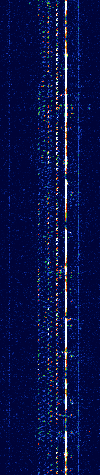 |
||
| WEFAX | Radiofax (Also known as Weatherfax, HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz)-FAX, WEFAX, and Weather Facsimile) is a slow scan analog image transmission mode used for the transmission of weather charts and meteorological reports. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMFrequency Modulation | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 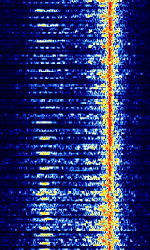 |
|
| WLO | AMAmplitude Modulation | CWContinuous Wave | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
|||
| WSPR | Weak Signal Propagation Reporter. | 136 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1,296.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 6 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 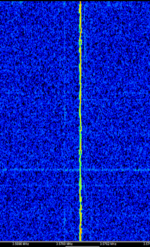 |
|
| WinDRM | WinDRM is an amateur radio derivation of the Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) digital voice and data transmission protocol. Also known as HamDRM, and Digital SSTV. | 14.236 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| XMPP trials | XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) on shortwave is used by the military and are known for using MIL 188-110A Serial HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) waveform and 6-bit code clear text with dual bursts of STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).-5439 and STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).-5066 as for XMPP Multi-User Chat (MUC) messages | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 7.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 34 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 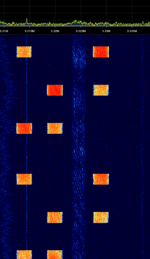 |
|
| Yachta T-219 Voice Scrambler | Yachta or Yakhta (Russian for 'Boat') T-219 is an analogue voice scrambler. It is unique in that an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying sync signal is transmitted in the middle of the main signal, with the scrambled voice stream split above and below the FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 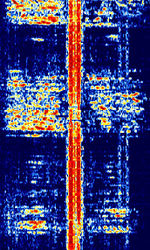 |
|
| Yugoslavian 16-Tone Modem | The Yugoslavian 16-Tone Modem, also known as YUG-Diplo 16-Tone, is a 16 tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing PSKPhase-Shift Keying modem used in former Yugoslavia for diplomatic use. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 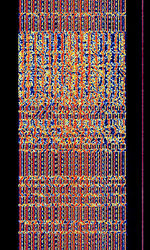 |
|
| Yugoslavian 20-Tone Modem | The Yugoslavian 20-Tone Modem, also known as YUG-MIL 20-Tone and YUG Diplo 20-Tone, is a 20 tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing PSKPhase-Shift Keying modem used in former Yugoslavia for military and diplomatic use. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 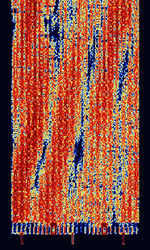 |
Pages in category "HF"
The following 200 pages are in this category, out of 265 total.
(previous 200) (next 200)(previous 200) (next 200)