Navigation
From Signal Identification Wiki
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'Vario' Airplane Data Controller | This transmitter is found within the UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) FMRS bands, most likely used at airshows to give off barometric pressure, height in altitude represented by a voice, including various tones representing how high/how low the model plane is in the air. | 462.61 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 462.725 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 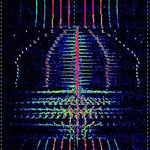 |
||
| Accurate positioning by Low Frequencies (ALF) | Accurate positioning by Low Frequencies, a former German DGPS navigation system. No longer in use as of 2013. | 123.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Germany | 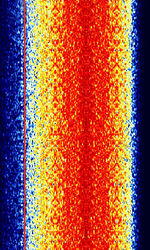 |
|
| BRAS-3 (RS-10) | BRAS-3 and the closely related RS-10 are Russian medium frequency hyperbolic navigation systems used for marine navigation | 1.685 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 2.107 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, Pulse | 14 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 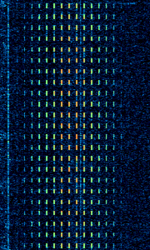 |
|
| DeltaFix | DeltaFix was a DGPS system that was used to provide precision positioning used in the survey and oceanographic industry. | 1.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 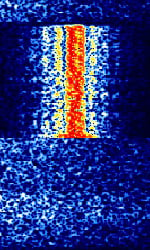 |
|
| Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) | Differential GPS (DGPS), also known as M823 DGPS and SC-104 DGPS, is a supplementary correction signal used by GPS receivers to increase the accuracy of GPS based positioning. | 283.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 150 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 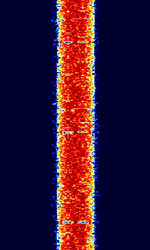 |
|
| Eurobalise downlink | Downlink from train to balise. A Eurobalise is a specific variant of a balise, a transponder placed between the rails of a railway. | 27.095 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Europe | 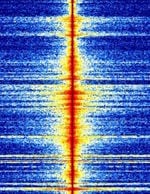 |
|||
| Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) | GBAS is an advanced aircraft navigation system that provides GPS corrections to aircraft on approach. | 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 117.975 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | D8PSK | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 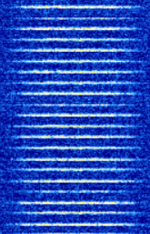 |
|
| HyperFix | HyperFix was a radio-navigation system developed by Racal. Was used by vessels and ships. Has largely been phased out in favor of Differential GPS. | 1.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 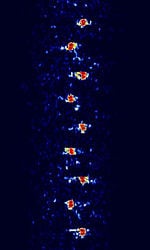 |
||
| Instrument Landing System | Radio navigation system that allows aircraft to perform precision approaches in low visibility conditions. | 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 335 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
||
| John Deere RTK Radio 450 | Real-time Kinematic GPS is a satellite navigation technique used to enhance the precision of position data derived from satellite-based positioning systems (global navigation satellite systems, GNSS) such as GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS, Galileo and NavIC. | 435 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 7.49 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 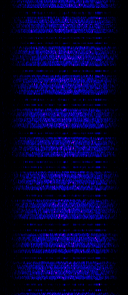 |
|
| LORAN | LORAN (short for LOng RAnge Navigation) is a hyperbolic radio navigation system. | 90 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 110 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PPMPulse Position Modulation | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 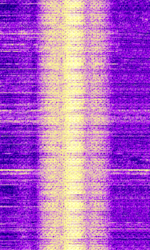 |
|
| NDB beacon signals | Non-directional Beacons are low frequency navigation aids | 290 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 421 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Brussels, Belgium | 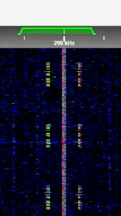 |
||
| Non-Directional Beacon (NDB) | A Non-Directional Beacon (NDB) is a ground-based, low frequency radio transmitter used as an instrument approach for airports and offshore platforms. | 190 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | AMAmplitude Modulation | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Primary Aeronautical Surveillance Radar | A Primary radar (PSR Primary Surveillance Radar) is a conventional radar sensor that illuminates a large portion of space with an electromagnetic wave and receives back the reflected waves from targets within that space. | 1,215 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | Pulse | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 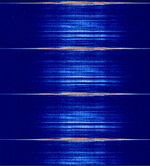 |
|
| Radio Navigation Satellite System (RNSS) | Generic positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) signals transmitted by global/regional navigation satellite system (GNSS/RNSS) and Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) constellations such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, QZSS, and IRNSS. | 1,176.45 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,575.42 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, DSSS, BOC, TMBOC | 22 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Radioteknicheskaya Systema Dalney Navigatsii (RSDN-20) | RSDN-20, also known as Alpha, is a Russian hyperbolic radio navigation system. Presumed to be used for Russian ships, submarines and aircraft in the northern hemisphere, possibly worldwide. | 11.91 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 14.88 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | 20 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia |  |
||
| Secondary surveillance radar (SSR) | Secondary surveillance radar (SSR)is a radar system used in air traffic control. A surveillance radar system which uses transmitters/receivers (interrogators) and transponders. | 1,030 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | PPMPulse Position Modulation | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 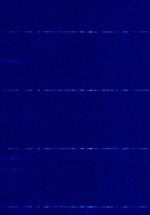 |
|
| Sonne | Sonne (Called Consol by the Britons) was a low-frequency radio range based radio navigation system used for long range navigation. | 250 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 350 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 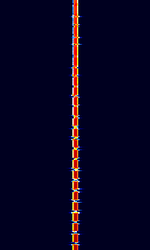 |
|
| Tactical Air Navigation System (TACAN) | Radio navigation technology that measures the slant range (distance) between an aircraft and a ground station by timing the propagation delay of radio signals. | 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,213 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | PAMPulse Amplitude Modulation | Worldwide | 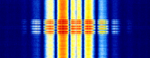 |
|||
| Transit 5B-5 | Transit 5B-5, a former TRANSIT navigation satellite, is the oldest satellite known to still transmit a signal. Considered "dead" because its navigational systems failed after 19 days of operation, it still emits a telemetry signal when illuminated. | 136.658 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | PCM, PAMPulse Amplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation, PM | 32 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 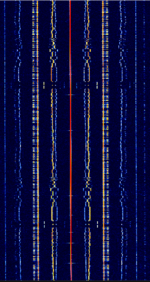 |
|
| VHF Omnidirectional Range (VOR) | A type of radio navigation system used by aircraft. It is distinctive in that the center frequency is flanked by two FMFrequency Modulation waves. | 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 117.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 21 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 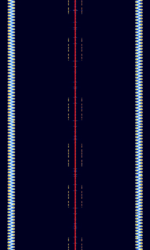 |
Pages in category "Navigation"
The following 21 pages are in this category, out of 21 total.
'ABDE |
GHIJLNP |
RSTV |