Inactive/Rare Signals
From Signal Identification Wiki
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1G (NMT) Nordic Mobile Telephone | Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT, NMT-450, and NMT-900) is a first generation analog cell phone system. Originally designed for and by Nordic countries (Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark) it was widely deployed around the world. Nowadays (as of 2015) NMT is defunct. | 453 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 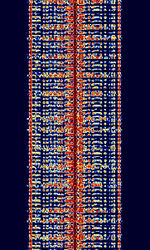 |
|
| 1G Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) | The first generation of cellular mobile telecommunications, which used analogue NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation voice. | 824 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 894 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 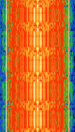 |
|
| 2G CDMA (IS-95) | CDMACode Division Multiple Access-One also known as IS-95, was the first ever cellular standard technology based on Code Division Multiple Access (CDMACode Division Multiple Access). It is a predecessor of the 1xRTT (CDMA2000/IS-2000) standard, which is backwards compatible. | 815 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,995 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | DSSS/QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 1.228 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 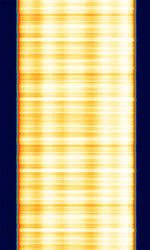 |
|
| AMSAT-P3D | AMSAT-P3D (Known as Phase 3D, OSCAR-40, and AO-40) is a amateur radio satellite built by AMSAT. As of 2004, the satellite's systems have failed. | 145.805 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 24,048.285 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 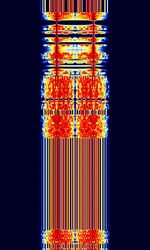 |
|
| ARQ-M2-242 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M2-242 (Also known as TDM 242, TDM-2, 96-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-28) is a two-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 242 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Marine, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 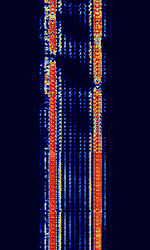 |
|
| ARQ-M2-342 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M2-342 (Also known as TDM 342, TDM-2, 96-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-28) is a two-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 342 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 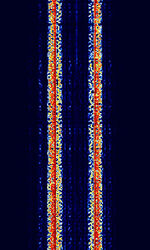 |
|
| ARQ-M4-242 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M4-242 (Also known as TDM 242, TDM-4, 192-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-56) is a four-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 242 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 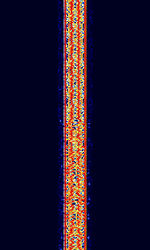 |
|
| ARQ-M4-342 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M4-342 (Also known as TDM 342, TDM-4, 192-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-56) is a four-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 342 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 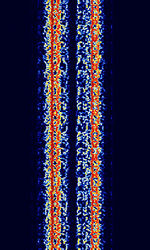 |
|
| ARQ-N | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-N is a synchronous dual channel ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query mode identical to ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-E, with the only difference being that ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-N has no symbol inversions. Formerly used by Italian Diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 850 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 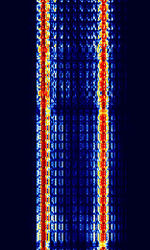 |
|
| ARQ6-90 | ARQ6-90, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-6-90 and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-6/90, is a 6-character block simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system formerly used by French and Italian diplomatic services exchange of teletype-data. It is no longer used or seen today. | 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 700 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 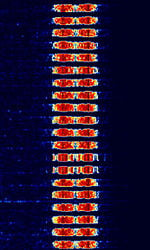 |
|
| ARQ6-98 | ARQ6-98, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-6-98 and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-6/98, is a 6-character block simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system formerly used by French and Italian diplomatic services for the exchange of teletype-data. It is no longer used or seen today. | 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| AUTOSPEC | AUTOSPEC is a synchronous FECForward Error Correction teletype system used by British coastal stations to communicate with North Sea oil rigs. Also known as Autospec-bauer, Bauer, and Autospec Mk1. This signal is most likely phased out. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 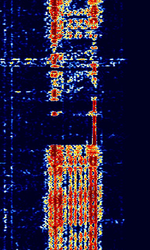 |
|
| Accurate positioning by Low Frequencies (ALF) | Accurate positioning by Low Frequencies, a former German DGPS navigation system. No longer in use as of 2013. | 123.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Germany | 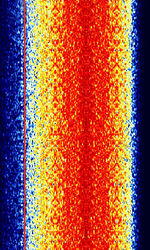 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) | Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) is a DRM-based radiotext and data technology for AMAmplitude Modulation broadcasting, like RDS that is used for FMFrequency Modulation. It transmits as a subcarrier, phase-modulating the carrier frequency. | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 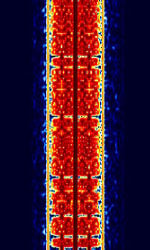 |
||
| Automatic Link Set-up (ALIS) | Automatic Link Set-up (ALIS) is an automatic link system used by Rohde & Schwarz modems. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 270 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 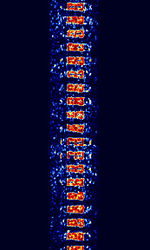 |
|
| Automatic Picture Transmission (APT) | Automatic Picture Transmission (APT), also known as NOAA-GEOSAT, was an analog image transmission mode used by the NOAA weather satellites and some Russian weather satellites to transmit satellite weather photos. As of august 2025, most of the NOAA sats that transmitted this mode have been decommissioned, and have discontinued transmission. | 137.1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 137.913 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 34 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 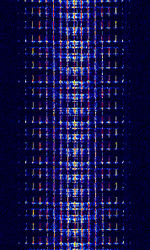 |
|
| B-Netz | B-Netz, was an analog, commercial mobile radio telephone network that was operated by the Deutsche Bundespost in Germany (at first only West Germany) from 1972 until 1994. The system was also implemented in neighboring countries Austria, The Netherlands and Luxembourg. | 148 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 153 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 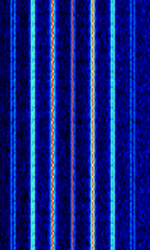 |
|
| BR-6028 | BR-6028 is a VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy (Voice Frequency Telegraph) frequency and time diversity modem using 7 data channels. It is sometimes also known as BARRIE, USA-7, or 6028. | 5.75 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15.937 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 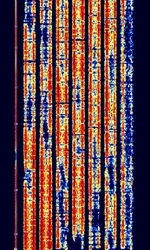 |
|
| CAS-4A/B Satellite Telemetry | CAS-4A/B Satellite 4.8 kbpsKilobits per second (kbps) GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying Telemetry Downlink. | 145.835 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 145.89 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 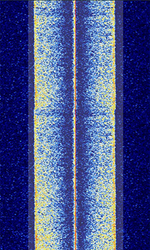 |
|
| CHIP | CHIP is a spread-spectrum PSKPhase-Shift Keying mode developed by Antonino Porcino IZ8BLY. CHIP-64 runs at 37.5 bpsBits per second (bps), whereas CHIP-128 runs at 21.09 bpsBits per second (bps). | 7.09 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.11 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 580 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 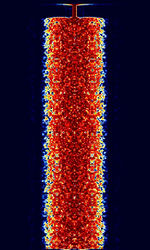 |
|
| CIS 3x100 VFT | Three CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-14 signals overlaid on top of each other in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth, operating at 100 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia |  |
|
| CIS 3x144 VFT | Three 144 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signals in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth. Reportedly phased out. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 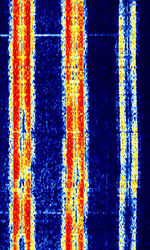 |
|
| CIS 3xBaudot-50 VFT | Three 50 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. Baudot signals in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 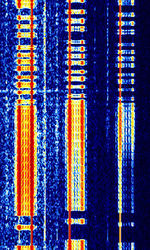 |
|
| CIS-11 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-11 (Also known as TORG-11) is a radio duplex teleprinter system used by Russian meteorological stations | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 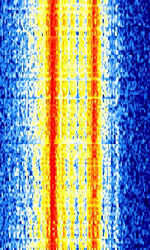 |
|
| CIS-1280 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-1280 is a OQPSK (Offset Quadrature Phase Shift-Keying) modulation data modem signal. Also known as Soviet Mil(MOD)/FAPSIFederal Agency of Government Communications and Information (Russian Agency)/PTTPush To TalkPress to TransmitMinistries of Postal, Telephone, and Telegraph Service (Soviet Agency) system. These stations are recognizable in that they are all placed on .081 offsets from a kilohertz or half kilohertz point. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 13.369 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.28 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 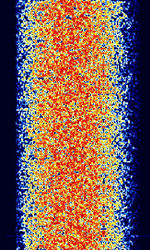 |
|
| CIS-14 | Also known as AMOR and AMOR96. Synchronous FSKFrequency-Shift Keying duplex teleprinter system with ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 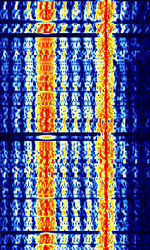 |
|
| CIS-16 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-16 is a BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) 16-tone mode, possibly transmitted from a modified AT-3004D or AT-3104 type Russian military transceiver. Also known as CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic 16x75 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. for the 75 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. speed in each of the 16 sub channels. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 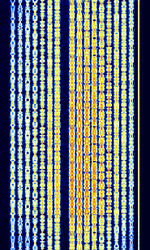 |
|
| CIS-300 | Known as CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-300 Burst, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode used with 300 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. rate with a starting and ending tone on the upper part of the signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 370 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 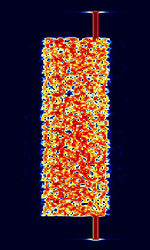 |
|
| CIS-40.5 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-40.5 (Also known as T-206) is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal used in Russian Military Communications Equipment. Used as a telegraph channel, encrypted. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 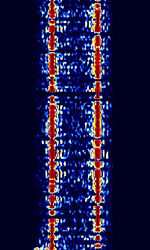 |
|
| CIS-8181 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-8181 is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying modem used by the Russian navy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 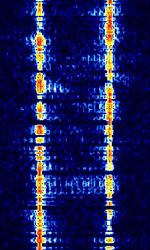 |
|
| CLOVER-I | CLOVER-I was the first iteration of the Clover series of digital modes. Was never released for commercial use, replaced by CLOVER-II. Also known as Cloverleaf. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 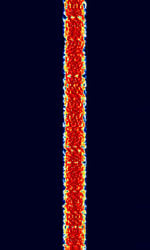 |
|
| CRY2001 Voice Scrambler | CRY2001 is a voice scrambling mode used on Sailor CRY2001 Scramblers. Fisherman often use these modes to communicate with privacy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 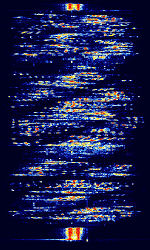 |
|
| CV-786 | CV-786 is a wideband FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode built in Rockwell-Collins MDM-2001 modems. Also known as TRC-75, as it was used in TRC-75 transceivers. A military-based Radio TeleTYpe mode. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 900 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 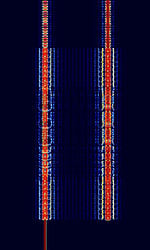 |
|
| Coherent BPSK | Coherent BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), also known as C-BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), was an experimental amateur mode developed by Bill DeCarle VE2IQ. | 138 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 18.081 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 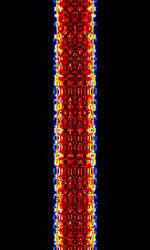 |
|
| Coherent CW | Coherent CWContinuous Wave (also known as CCW) was a strictly timed morse code mode designed by Ray Petit W7GHM (The same inventor of CLOVER). CCW depended on accurate timing from both receiver and transmitter. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Coquelet | Coquelet is an MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying system, similar to Piccolo. Also known as COQ-8, COQ-12, and COQUELET 8 V 2. Uses ITA-2 charset. It's two main modes are Coquelet-8 and Coquelet-13. No longer in use. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 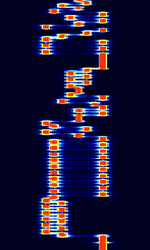 |
|
| DUP-ARQ | DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as ARTRAC and 125-ARTRAC, is a semi-duplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system once used by Thai and Hungarian Diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 325 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| DUP-ARQ-2 | DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-2 (also known as ARTRAC II) is a further development of the DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system and the system characteristics are very similar. DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-2 allows transmission of ITA-2 (Baudot) or ITA-5 (ASCII) characters depending on the application. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| DUP-FEC-2 | DUP-FECForward Error Correction-2 is a further development of the DUP-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system and the system characteristics are very similar. Uses FECForward Error Correction instead of ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query and runs at either 125 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. or 250 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Delfi-C3 Telemetry | Delfi-C3 Telemetry was a telemetry signal sent from the Delfi-C3 university-class satellite. | 145.87 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | LSBLower Side Band Modulation | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 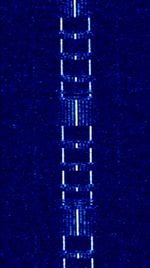 |
|
| DeltaFix | DeltaFix was a DGPS system that was used to provide precision positioning used in the survey and oceanographic industry. | 1.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 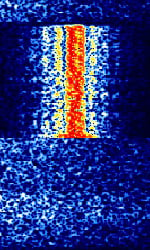 |
|
| DominoEX | DominoEX, also known as just Domino, is an IFKIncremental Frequency Keying (Incremental Frequency Keying) mode developed by Murray Greenman ZL1BPU and Con Wassilieff ZL2AFP in 2004 that was the first fully developed iteration of the Domino IFKIncremental Frequency Keying family modes. Used to send text over RFRadio Frequency. | 5.332 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.117 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IFKIncremental Frequency Keying | 173 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 524 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| DominoF | DominoF was the first experimental implementation of the Domino family of IFKIncremental Frequency Keying modes, developed by Con ZL2AFP. DominoF used dual interleaved tone sets. Superseded by DominoEX. | 1.838 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.08 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IFKIncremental Frequency Keying | 220 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Duga 3 | Duga (Russian: Дуга́) was a Soviet over-the-horizon radar system used as part of the Soviet missile defense early-warning radar network. The system operated from July 1976 to December 1989. Two operational Duga radars were deployed, one near Chernobyl and Chernihiv in the Ukrainian SSR (present-day Ukraine), the other in eastern Siberia. The Duga systems were extremely powerful, over 10 MW in some cases, and broadcast in the shortwave radio bands. They appeared without warning, sounding like a sharp, repetitive tapping noise at 10 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., which led to it being nicknamed by shortwave listeners the Russian Woodpecker. | 7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 19 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 800 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Ukraine | 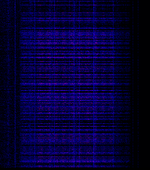 |
|||
| Emergency Managers Weather Information Network (EMWIN) - Repeater | The Emergency Managers Weather Information Network (EMWIN) is a system for distributing a live stream of weather information in the United States. This is the VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) Repeater of the network. | 163.3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 168.813 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 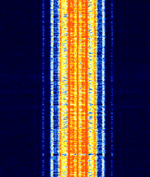 |
|
| European Radio Message System (ERMES) | European Radio Message System (ERMES) is a European common standard for paging developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ESTI) | 169.413 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 169.833 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 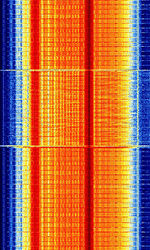 |
|
| FEC-A | FECForward Error Correction-A, also known as FECForward Error Correction-100 or FECForward Error Correction-100A, is a synchronous simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system that uses the ITA 2 alphabet. This mode was once used by many embassies, diplomatic services, and news agencies worldwide. This mode was developed by Siemens. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 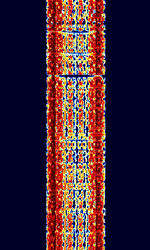 |
|
| FLASH-OFDM | Fast Low-latency Access with Seamless Handoff Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (FLASH-OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing) is a mobile data access technology developed by Flarion. | 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | MC-CDMACode Division Multiple Access | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Finland, Slovakia, Germany, United States | 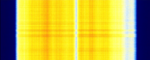 |
|
| FSK441 | FSK441 is a high speed meteor scatter communication mode. FSK441 uses a baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. rate of 441 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 144 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 444 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 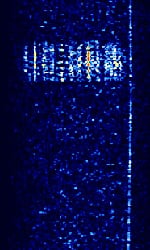 |
|
| FST4 | FST4 is a 4-GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying amateur radio communications mode, designed especially for making contacts (QSO's) on LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) and MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz) frequency ranges under extreme weak-signal conditions. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | 137 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 474 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 66 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 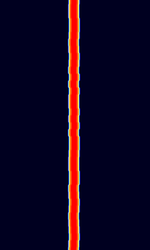 |
|
| FreeDV plus Video | FreeDV plus Video (also known as FreeDV+) combines analog FMFrequency Modulation multicarrier Narrow Band TV (NBTV) by Con Wassilieff, ZL2AFP, and FreeDV digital voice by David Rowe, VK5DGR. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, FMFrequency Modulation | 3.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 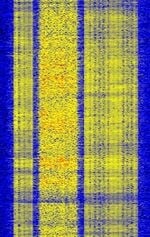 |
|
| Frequency Division Multiplex Digital Voice (FDMDV) | Frequency Division Multiplex Digital Voice (FDMDV), also known as FDMDV 14+1-tone, is a digital voice mode originally developed by Peter Martinez G3PLX and Francesca Lanza HB9TLK. It has since been improved upon by David Rowe. (FreeDV COHPSK) | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.125 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 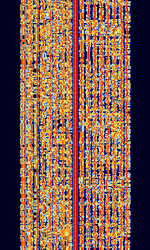 |
|
| G-TOR | Golay-Teleprinting Over Radio (G-TOR) is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying proprietary standard developed by Kantronics Inc. and is used by radio amateurs, military (Irish Air Corps/Navy, Mexican army) and governmental agencies (ICRC). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 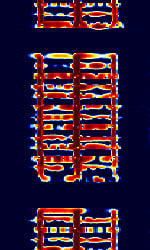 |
|
| Gandalf MDT | Gandalf MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office. was developed by Gandalf Mobile Systems, a subsidiary of Canadian company Gandalf Technologies. Used primarily by taxi and courier services in Canada and the United States. This protocol was used in Gandalf's Cabmate systems. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 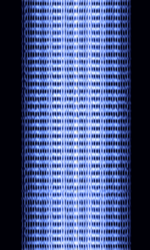 |
|
| Globe Wireless HF Network | Globe Wireless' Maritime Digital Radio was a system of 24 stations around the globe offering data services to large cargo vessels. Since 2014, GW has discontinued their HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) network. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Golay Paging (GSC) | Golay Paging (or Golay Sequential Code, GSC) is a one-way 2-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying paging format developed by Motorola. It is capable of transmitting tone, numeric, alphanumeric, and voice pages. | 33 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 932 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 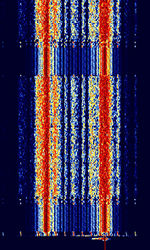 |
|
| Graw DFM-06 Weather Balloon (Radiosonde) | The DFM-06 is a standard radiosonde for most applications. It is perfectly suited for synoptic observations or military applications. | 400.01 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 405.99 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 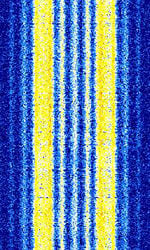 |
|
| HC-ARQ | Haegelin Crypto ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query (HC-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query) was an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying synchronous simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system used by the UN and International Rescue Committee. This mode has been phased out and is no longer in use. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 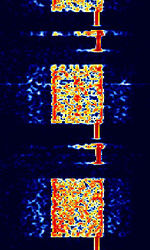 |
|
| HNG-FEC | HNG-FECForward Error Correction was a full duplex system developed and used solely by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Hungary. Used 100.05 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. with 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). shift FSKFrequency-Shift Keying. This mode is no longer used today. | 2.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 24 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Hungary | 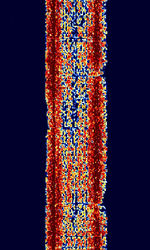 |
|
| High Power Auroral Stimulation (HIPAS) | The HIPAS (HIgh Power Auroral Stimulation) Observatory was a research facility, built to study the ionosphere and its influence on radio communications. It was located 25 miles east of Fairbanks, Alaska in the Fairbanks North Star Borough area. | 2.85 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4.53 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States | — |  |
|||
| HyperFix | HyperFix was a radio-navigation system developed by Racal. Was used by vessels and ships. Has largely been phased out in favor of Differential GPS. | 1.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 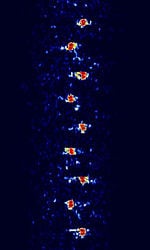 |
||
| IRA-ARQ | IRA-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as BULG-ASCII and ASCII-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, is a high data rate ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query FSKFrequency-Shift Keying system used by Bulgarian, Slovakian, and Czech diplomatic stations. The maximum speed of this mode has been seen to reach 1200 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. Not seen much much nowadays | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.35 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 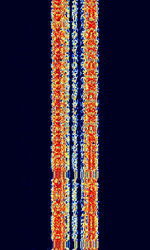 |
|
| IS-54 D-AMPS | D-AMPS, also known as IS-54 and IS-136, is a second generation (2G) mobile phone system standard which develops on analog AMPS, a 1G standard. This system is also colloquially known as TDMATime Division Multiple Access. | 824 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 894 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 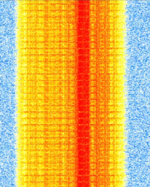 |
||
| ISCAT | Ionospheric Scattering (ISCAT) mode used for weak signal long distance radio contact by meteor and Ionosphere scattering. | 50 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 148 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 904 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.809 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 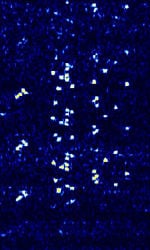 |
|
| Inmarsat IsatM2M | IsatM2M Service operated by Inmarsat on existing Inmarsat-D/D+ infrastructure. | 1,525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,559 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.024 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 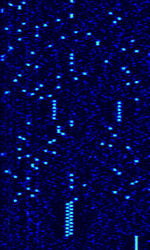 |
|
| Integrated Digital Enhanced Network (iDEN) | iDEN is a TDMATime Division Multiple Access-based digital wireless standard developed by Motorola. It is a type of trunked radio with cellular phone benefits. | 806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 869 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, TDMATime Division Multiple Access | 18.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 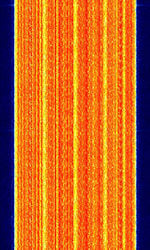 |
|
| JT4 | JT4 is a 4-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying extreme weak-signal mode which is designed especially for Earth-Moon-Earth communications. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 17 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 949 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
||
| JT6M | JT6M is part of the WSJT suite of digital weak signal software applications developed by Joe Taylor, K1JT | 50.215 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 50.25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 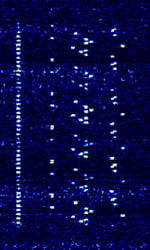 |
|
| JT9 | JT9 is a 9-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode for making contact (QSO's) under extreme weak-signal conditions. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | 3.578 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.079 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 16 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.78 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 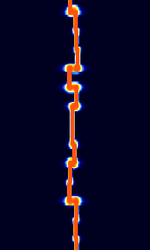 |
|
| JTMS | JTMS is a meteor scatter mode that uses MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.). JTMS behaves similarily to FSK441. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 1.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 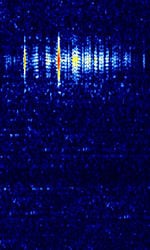 |
|
| Kiwi | Kiwi is a telemetry mode developed by CNES used on amateur rockets and radio balloons in France. | 137.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 138.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | France | 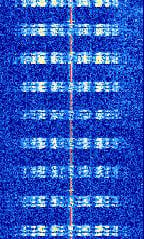 |
|
| Lentus | Lentus is an extremely slow QRPIn amateur radio, QRP operation refers to transmitting at reduced power while attempting to maximize one's effective range. mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE used to transmit QRPIn amateur radio, QRP operation refers to transmitting at reduced power while attempting to maximize one's effective range.'s at very low power. Each 43-character (75 bit) transmission takes roughly 5 minutes to transmit across 32 possible tones in a tight 25 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). bandwidth. | 136.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 14.096 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 25 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 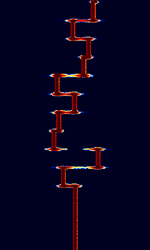 |
|
| MD-522 | MD-522 (Also known as MIL-M-55529A) is a synchronous FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode built into GRC-MD522 teletypewriter sets and used for wirelessly transmitting ASCII information. MD-522 has a narrowband, wideband, and diversity mode. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 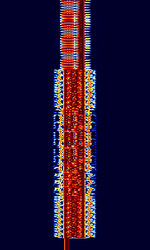 |
|
| MD-674 | MD-674, also known as Wireline FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, is a very old United States Military FSKFrequency-Shift Keying Modem from the 1960's. Uses 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). FSKFrequency-Shift Keying shift. Speeds of 50 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 75 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 100 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., and 150 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. have been logged. No longer seen today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States |  |
|
| MIL-STD-110-342 | MIL-STD-110-342 was a US Dept. of Defense standard for a 16 channel VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy teletype transmission. This mode was officially cancelled as of December 5th, 1995. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 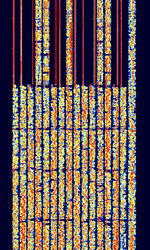 |
|
| MMP-4800 | MMP-4800 was a MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office. (Mobile Data Terminal) protocol developed by Canadian company Mobile Data International (MDI) in 1982 for their Mobile Data Terminals. Used by public safety and commercial industries. Phased out. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 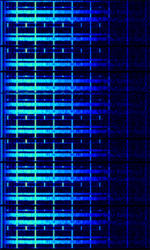 |
||
| Marconi Selenia 25-Tone Modem | The Marconi Selenia 25-Tone Modem is a military modem developed sometime around 2003 by Marconi Selenia Communications (Now Finmeccanica). It supports ECCMElectronic Counter-CounterMeasures (ECCM) is a part of electronic warfare which includes a variety of practices which attempt to reduce or eliminate the effect of electronic countermeasures (ECM) such as jamming. ECCM is also known as electronic protective measures (EPM), chiefly in Europe. capability and transmits at a datarate of 2400bps. This mode was employed by Turkey. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 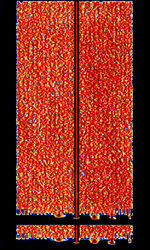 |
|
| Meteosat WEFAX | Meteosat WEFAX is a WEFAX used to transmit satellite images via Meteosat Satellites. WEFAX was introduced with the first Meteosat in 1977. | 1,691 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | Worldwide | 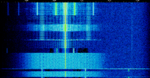 |
||
| Motorola SECURENET | Motorola SECURENET ("analog" encryption) was a secure voice option for conventional and Motorola Type II trunked systems, encoding the voice using 12kbps CVSD and encrypting the bitstream. It is easily identified by the 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz tone at the end of transmission. As it is not 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz FCC narrowbanding mandate compliant, it does not see much use anymore. | 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 16 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 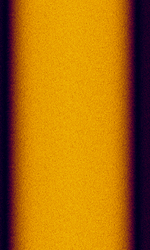 |
|
| Multiple sub-Nyquist Sampling Encoding (MUSE) | Multiplite sub-Nyquist Sampling Encoding (MUSE) also known as Hi-Vision was a early analogue high-defition television standard developed by NHK Science and Technical Research Laboratories. Replaced by digital ISDB broadcast since 2007. | 8,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | FMFrequency Modulation, DPCM, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation | 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 27 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| Multiplexed Analogue Components (MAC) | Multiplexed Analogue Components (MAC/packet) family was a analogue television broadcasting standard. Replaced by digital broadcast. | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation, AMAmplitude Modulation, 2PSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), 4PSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 7.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 22 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| NOAA Direct Sounder Broadcast (DSB) | The Direct Sounder Broadcast (DSBDual Side Band Modulation) is an auxiliary telemetry downlink from NOAA Polar Operational Environmental Satellites (POES), transmitted alongside Automatic Picture Transmission (APT) broadcasts. | 137.35 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 137.77 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 33.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 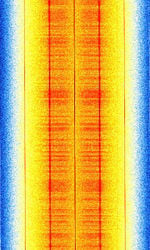 |
|
| NOAA ITOS High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) | An analog signal broadcast from NOAA ITOS polar satellites that transmitted images from the VHRR radiometer. | 1,697.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 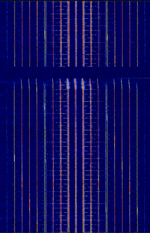 |
|
| NOAA POES High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) | A digital link to transmit images and other data collected from the satellite at a high resolution. | 1,698 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 2,247.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| NTSC Broadcast | National Television System Committee (NTSC) Television broadcast is an analogue television broadcast mode. Currently being phased out in parts of the world in favor of digital broadcast. | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 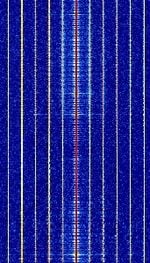 |
|
| OpenSky | OpenSky is an encrypted TDMATime Division Multiple Access protocol that is heavily used but is being phased out by the Pennsylvania State Police. No one other than the intended user has been able to decrypt the signal. | 700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | TDMATime Division Multiple Access, 4GFSK | 20.07 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 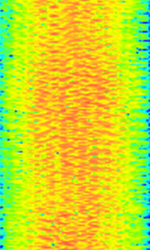 |
|
| PACTOR I | PACTOR-I is a digital data protocol combining elements of PACKET and AMTOR ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 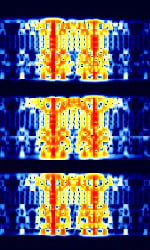 |
|
| PAL Broadcast | Phase Alternating Line (PAL) Analogue Television Broadcast. Now phased out in most of the world. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 862 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 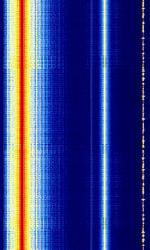 |
|
| PAX | PAX and PAX2 are developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2005, and was derived from Olivia. It utilizes the AX.25 protocol that PACKET uses, and had a minimum SNR of -10dB. Can transmit APRSAutomatic Packet Reporting System, an amateur radio-based system for real time tactical digital communications of information of immediate value in the local area frames. | 3.59 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.62 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 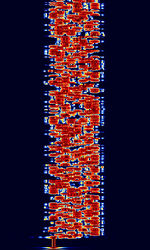 |
|
| POL-ARQ | POL-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query was a duplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system used by Polish and Italian diplomatic services. This system uses the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 476-4 alphabet with polatiry retained. No longer in use. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe | 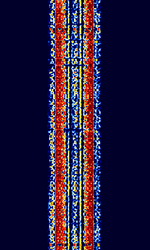 |
|
| PRC-16 | PRC-16 is a Chinese sourced PSKPhase-Shift Keying data link, traced to Shanghai. Suspected user Chinese Military. | 14.3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 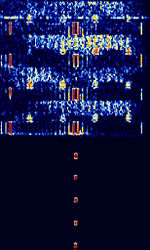 |
|
| PSK-AM | PSKPhase-Shift Keying-AMAmplitude Modulation is an amateur digital mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2002/2003, and incorporates FECForward Error Correction interleaving. PSKPhase-Shift Keying-AMAmplitude Modulation uses the modulation of PSK10/31 with the FECForward Error Correction of SITOR-B. | 10.148 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.62 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 40 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 180 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| PSK2K | PSK2K is a meteor scatter type of mode written by DJ5HG Using a modulation scheme of BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) at 2000 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 50.36 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.36 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 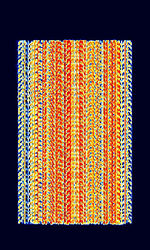 |
|
| Piccolo | Piccolo was a MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying system developed by the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO) to communicate with foreign embassies and UK military stations around the world. No longer used. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 180 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 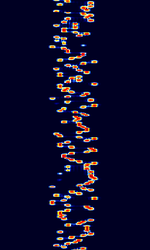 |
|
| Polish Intelligence 100bd 625Hz FSK | Also known as F11, this is a one-way broadcast system that was used by one of Polish intelligence agencies for delivery of messages to their operatives abroad on fixed schedules. | 4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Poland | 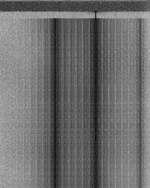 |
|
| Q-MAC HF Modem | The Q-MAC HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Modem is a military modem developed by Q-MAC (acquired by Barrett Communications). It uses OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing with a BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) sync channel in a gap of the signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, PSK8 | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 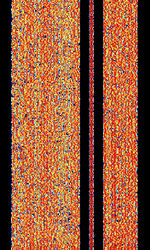 |
|
| Q15X25 | Q15X25, also known as NEWQPSK, is an experimental amateur radio packet modem developed by Pawel Jalocha SP9VRC. Q15X25 is a OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) implementation of the AX.25 Packet protocol used in PACKET. | 3.585 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.109 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.95 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.35 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 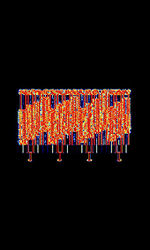 |
|
| RAC-ARQ | RAC-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as MEROD and RACAL-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, is a teleprinter system by Racal, used in MEROD devices. MEROD stands for Message Entry and Read Out Device. Hasn't been seen since 2010. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 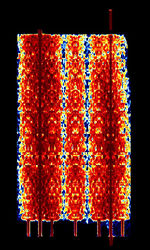 |
|
| RTTYM | RTTYM, developed by Nick Fedoseev (UT2UZ) in 2005, is a digital mode derived from Olivia. It aims to deliver a compromise of speed and performance. RTTYM is about 4x faster than Olivia, but trades the speed for reduced robustness and sensitivity. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 150 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 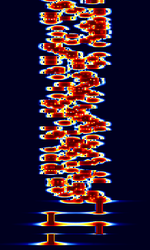 |
|
| RUM-FEC | RUM-FECForward Error Correction, also known as ROU-FECForward Error Correction and SAU-FECForward Error Correction, is a FSKFrequency-Shift Keying FECForward Error Correction system used by Romanian diplomatic services. This is no longer used today, replaced by MIL-STD 188-110 Serial. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 750 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Romania | 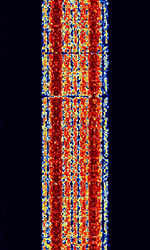 |
|
| RUM-MOI FEC | RUM-MOI FECForward Error Correction, also known as RUM-MIL 115.76 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., is a FSKFrequency-Shift Keying FECForward Error Correction mode used by the Romanian Ministry of Internal Affairs, supposedly under military use. This is no longer used today, replaced by MIL-STD 188-110 Serial. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Romania | 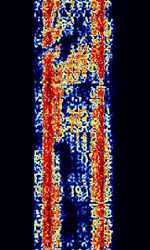 |
|
| Radio Telephone Network C (C-Netz) | The Radio Telephone Network C (German: Funktelefonnetz-C, abbreviated as C-Netz), was a first generation analog cellular phone system deployed and operated in Germany (at first West Germany) by DeTeMobil (formerly of Deutsche Bundespost Telekom, currently Deutsche Telekom). | 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Germany | 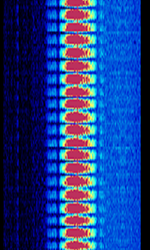 |
|
| Redundant Digital File Transfer (RDFT) | RDFT is an amateur radio digital mode used to transmit files. | 9.065 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 9.24 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 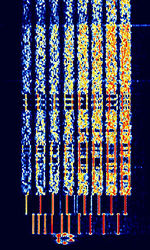 |
|
| Russian Diplo VFT PSK 64Bd | Russian Diplomatic 3 channel VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy PSKPhase-Shift Keying running at 64 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. Enigma M42 designation | 4.022 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 23.131 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 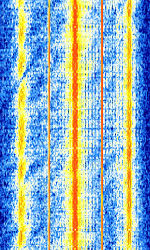 |
|
| SECAM | Sequential Colour with Memory (SECAM) Analogue Television Broadcast. Now phased out in most of the world. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 862 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 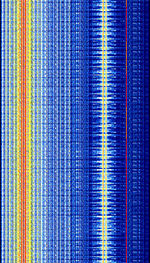 |
|
| SI-ARQ | SI-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-S and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-1000S, is a simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system designed by Siemens formerly used by Austrian and Indonesian diplomatic services. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe |  |
|
| SI-FEC | SI-FECForward Error Correction, also known as FECForward Error Correction-S, FECForward Error Correction 1000 Simplex, and FECForward Error Correction-1000S, was the FECForward Error Correction variant of SI-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, and was only used under extremely poor propagation conditions. SI-FECForward Error Correction was developed by Siemens and was used by Austrian and Indonesian diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 280 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe | 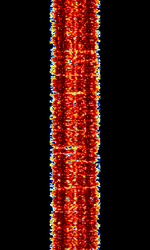 |
|
| SP-14 (XP) | SP-14 (XP) was a 14 tone MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode with origins from the Russian Intelligence and Foreign Ministry. Also known as NUM-13. Inactive since 2005, superseded by XPA. | 9 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia |  |
|
| SPREAD | SPREAD, also known as AUTOSPEC Mk2, SPREAD-11, SPREAD-21, and SPREAD-51, was a FECForward Error Correction system used by Romanian diplomatic stations and the Brazilian Navy and shore stations. SPREAD is considered the successor to AUTOSPEC. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 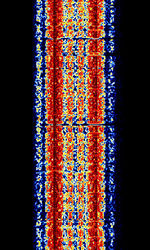 |
|
| STANAG 4415 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4415 is a NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization standard for robust, non-hopping digital data communication, used on severely degraded HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) channels with large Doppler and multipath spreads. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 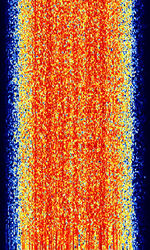 |
|
| SWED-ARQ | SWED-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-SWE, was a Swedish simplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system used by Swedish diplomatic services. This protocol supported three packet lengths and was able to change packet length mid-transmission. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Sweden |  |
|
| Sonne | Sonne (Called Consol by the Britons) was a low-frequency radio range based radio navigation system used for long range navigation. | 250 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 350 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 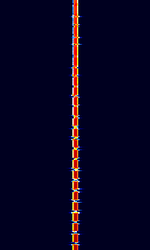 |
|
| THOR | THOR is an adaptation of DominoEX with MFSK16 binary varicode and FECForward Error Correction. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IFKIncremental Frequency Keying | 173 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 524 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 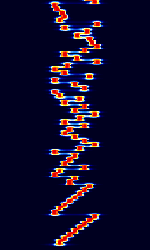 |
|
| THROB | THROB is a unique data mode that relies heavily on DSP techniques, using MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying and AMAmplitude Modulation modulation techniques together. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 72 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 188 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 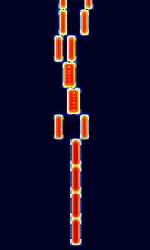 |
|
| TT2300 | TT2300, also known as TT2300B, TT2300-ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query, TRA-2300, and TPLEX, is an 8MFSK synchronous system developed by Thrane & Thrane of Denmark (acquired by UK defense firm Cobham in 2012). | 5.029 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 7.72 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 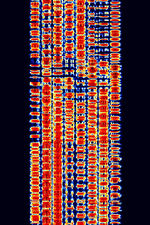 |
|
| TWINPLEX | TWINPLEX, also known as F7B4 and TWINPLEX-SITOR, was a diplex 4-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query mode developed by Mackay Radio and Telegraph Company, based in New York City, in the early 1950's. TWINPLEX was used by Interpol, the United Nations, and other diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 450 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 950 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Thales Système 3000 Skyhopper | Thales Système 3000 Skyhopper is the frequency hopping mode of the Système 3000 Modem. Characterized by it's very short bursts and frequency hopping behavior. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 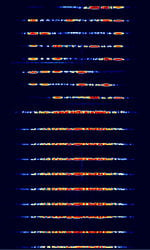 |
|
| The 'Air Horn' | "The Air Horn" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District, which also serves the same purpose as the buzzer. It was first heard in 2017, broadcasting on 4020 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz. 2 years later, in 2019, it changed to broadcast instead on 4070 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz (for about 2 months). A few months later, it was temporarily active on 3510 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz, before moving permanently to 3510 in October 2019. In December 2019, the channel marker broke down, and remained inactive until January 2020, broadcasting back on 3510 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz. In September 2022, it moved to 4930 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz, while broadcasting its first known voice messages almost a week after. After December 2023, the channel marker was replaced by The Goose's channel marker. It has not been heard since most likely December 2023 or very early 2024. The stations' last message was broadcasted in July 2023. | 4.93 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Smolensk, Russia | 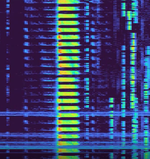 |
||
| The Alarm | Channel marker of a Russian military station nicknamed "The Alarm". "The Alarm" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District. So far, apart from test counts, it has not been heard with any actual traffic. | 4.77 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 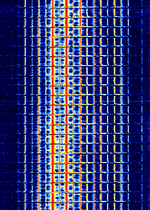 |
||
| The Goose | "The Goose" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District. It broadcasts on 4310 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz during daytime, changing to 3243 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz for nighttime. | 3.243 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4.31 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 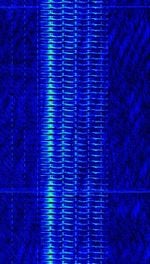 |
|
| Total Access Communication System (TACS) | A first generation analogue mobile cellular system which operated in the United Kingdom and a handful of other countries in Europe. It is also the EU's form of AMPS. | 872 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 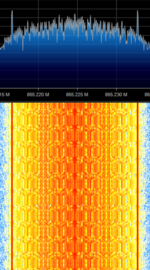 |
|
| VISEL | VISEL, also known as YUG-MIL 120.9 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., FECForward Error Correction-12, and YUG-MIL FECForward Error Correction, is a synchronous teleprinter system used by the former Yugoslav military. No longer active today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe | 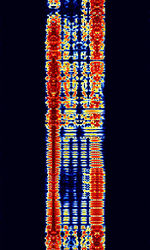 |
|
| VOICE | VOICE is a MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2006, and was derived from Olivia. It was designed for blind or partially sighted amateur radio operators. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 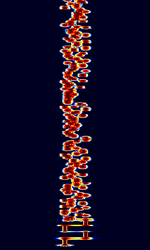 |
|
| Voice Inversion Scrambling | Analog Voice Inversion Scrambling divides the spectra into multiple bands and swaps them. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 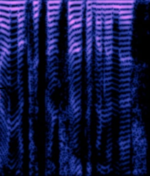 |
|
| WiMAX | WiMAX is a family of of wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) options. | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, OFDMA | 1.25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|||
| Yugoslavian 16-Tone Modem | The Yugoslavian 16-Tone Modem, also known as YUG-Diplo 16-Tone, is a 16 tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing PSKPhase-Shift Keying modem used in former Yugoslavia for diplomatic use. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 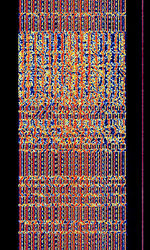 |
|
| Yugoslavian 20-Tone Modem | The Yugoslavian 20-Tone Modem, also known as YUG-MIL 20-Tone and YUG Diplo 20-Tone, is a 20 tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing PSKPhase-Shift Keying modem used in former Yugoslavia for military and diplomatic use. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 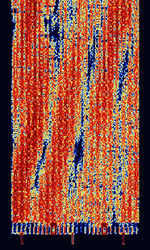 |
Pages in category "Inactive"
The following 129 pages are in this category, out of 129 total.