Medium Frequency (MF)
From Signal Identification Wiki
(Redirected from MF)
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz) encompasses frequencies from 300 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz to 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALE-400 | ALEAutomatic Link Establishment-400 is an amateur version of the 2G ALEAutomatic Link Establishment standard. It is adapted to the demands of amateur radio emergency traffic handling. | 1.806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.163 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 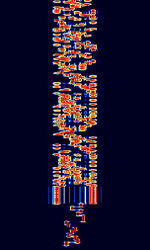 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation (AM) | Long range commercial broadcast and international radio. Also used for aviation communications. | 153 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 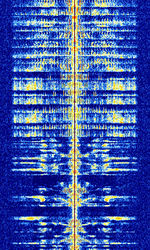 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) | Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) is a DRM-based radiotext and data technology for AMAmplitude Modulation broadcasting, like RDS that is used for FMFrequency Modulation. It transmits as a subcarrier, phase-modulating the carrier frequency. | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 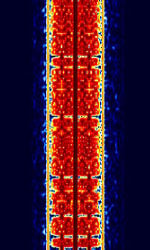 |
||
| Automatic Link Establishment (3G ALE ARCS) | 3G ALEAutomatic Link Establishment (ARCSAutomatic Radio Control System) is the next generation of ALEAutomatic Link Establishment (Designated by MIL-STD-188-141B (Appendix C)). Also known as STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4538, although MIL 188-141 does not provide Fast LSU. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 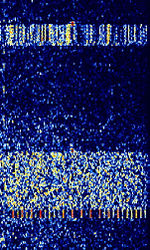 |
|
| BPM | BPM is a time signal transmitted by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, broadcasting from CAS's National Time Service Center in Pucheng County, China. | 2.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 3.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 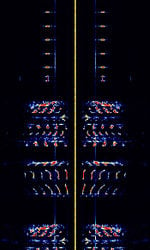 |
|
| BRAS-3 (RS-10) | BRAS-3 and the closely related RS-10 are Russian medium frequency hyperbolic navigation systems used for marine navigation | 1.685 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 2.107 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, Pulse | 14 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 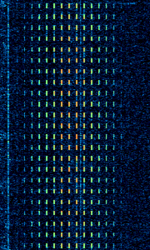 |
|
| CLOVER 2000 | CLOVER 2000 is an upgrade to CLOVER-II, a digital data protocol developed by Ray Petit and HAL Communications. Sometimes referred to as XCLOVER or 8 Tone CLOVER. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| CLOVER 2500 | CLOVER 2500 is a new upgrade to CLOVER-2000, adding 25% more speed to the CLOVER system. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| CLOVER-II | CLOVER-II is the advancement of CLOVER-I, with 4 tone pulses and a max data rate of 750 bpsBits per second (bps). Also known as Q-CLOVER and QUAD-CLOVER. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Coherent BPSK | Coherent BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), also known as C-BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), was an experimental amateur mode developed by Bill DeCarle VE2IQ. | 138 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 18.081 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 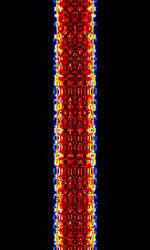 |
|
| DeltaFix | DeltaFix was a DGPS system that was used to provide precision positioning used in the survey and oceanographic industry. | 1.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 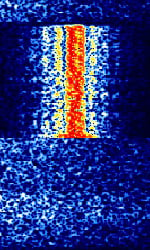 |
|
| Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) | Differential GPS (DGPS), also known as M823 DGPS and SC-104 DGPS, is a supplementary correction signal used by GPS receivers to increase the accuracy of GPS based positioning. | 283.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 150 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 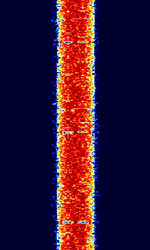 |
|
| Driftnet Buoy Radio Beacon | Driftnet Radio Buoys are extensively used by fishing boats operating in open seas and oceans for collecting long fishing lines or fishing nets, with the assistance of a radio direction finder | 1.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 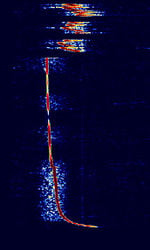 |
|
| FST4 | FST4 is a 4-GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying amateur radio communications mode, designed especially for making contacts (QSO's) on LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) and MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz) frequency ranges under extreme weak-signal conditions. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | 137 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 474 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 66 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 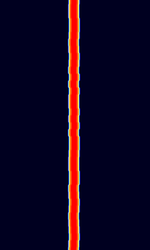 |
|
| FST4W | FST4W is an amateur radio digital protocol designed particularly for the LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) and MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz) bands, for quasi-beacon transmissions of WSPR-style messages. FST4W uses 4-GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying modulation and offers T/R sequence lengths of 120, 300, 900, and 1800 seconds. | 136 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.839 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 5 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 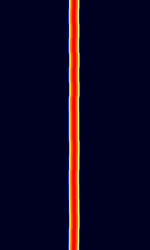 |
|
| HD Radio (AM) | HD Radio is a proprietary digital broadcast radio format transmitted in North America, usually as sidebands on analog carriers. This is the AMAmplitude Modulation band implementation of HD Radio. | 535 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 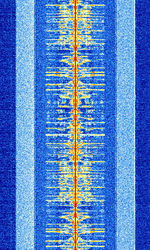 |
|
| High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program (HAARP) | HAARP is a ionospheric research program conducted in Gakona, Alaska. | 2.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation, CWContinuous Wave | CWContinuous Wave, FMCW | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
|
| High Power Auroral Stimulation (HIPAS) | The HIPAS (HIgh Power Auroral Stimulation) Observatory was a research facility, built to study the ionosphere and its influence on radio communications. It was located 25 miles east of Fairbanks, Alaska in the Fairbanks North Star Borough area. | 2.85 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4.53 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States | — |  |
|||
| HyperFix | HyperFix was a radio-navigation system developed by Racal. Was used by vessels and ships. Has largely been phased out in favor of Differential GPS. | 1.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 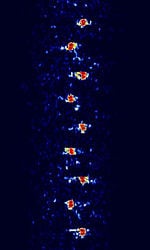 |
||
| Iranian 'Bubble' Jammer | Iranian broadcast jammer with characteristic sound. Used to suppress Radio Farda and other independent stations which broadcast to Iranian audience. | 1.547 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15.48 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 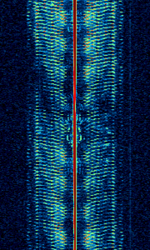 |
|
| JT9 | JT9 is a 9-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode for making contact (QSO's) under extreme weak-signal conditions. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | 3.578 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.079 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 16 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.78 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 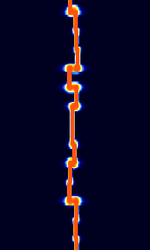 |
|
| Lentus | Lentus is an extremely slow QRPIn amateur radio, QRP operation refers to transmitting at reduced power while attempting to maximize one's effective range. mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE used to transmit QRPIn amateur radio, QRP operation refers to transmitting at reduced power while attempting to maximize one's effective range.'s at very low power. Each 43-character (75 bit) transmission takes roughly 5 minutes to transmit across 32 possible tones in a tight 25 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). bandwidth. | 136.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 14.096 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 25 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 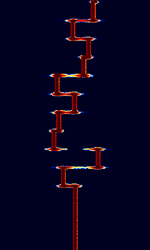 |
|
| Lightning Sferics | VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) RFRadio Frequency emissions from lightning in the atmosphere that can affect up to HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) frequencies and beyond depending on strength. Has a popping crackle sound with both USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) and AMAmplitude Modulation modes of reception. | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 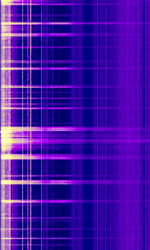 |
||||
| Link-11 | Link-11 (Also known as ALLIGATOR, STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5511, TADIL-A, MIL-STD-6011, and MIL-STD-188-203-1A) is a Tactical Data Link standard (formerly known as Tactical Digital Information Link (TADIL) used by NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization and the US Military for Maritime Tactical Data Exchange. | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 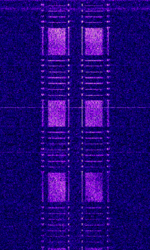 |
|
| Modernised High Frequency Communications System (MHFCS) | The Modernised High Frequency Communications System (MHFCS) is an Australian Department of Defense HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) System for their military communications network. Also known as AUS MIL ISBIndependent Side Band Modulation Modem, AUS MHFCS, and ADF HFCS. | 2.01 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 27.478 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 750 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Australia | 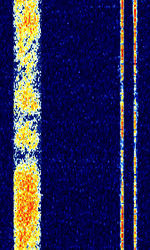 |
|
| Morse Code (CW) | CWContinuous Wave Morse Code is the simplest form of transmission found virtually all over the RFRadio Frequency bands for a variety of uses. The most common use of this is for Call-sign Beacons by both Amateur and Military operators. | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 250,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | Worldwide |  |
||
| NDB beacon signals | Non-directional Beacons are low frequency navigation aids | 290 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 421 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Brussels, Belgium | 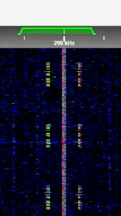 |
||
| Non-Directional Beacon (NDB) | A Non-Directional Beacon (NDB) is a ground-based, low frequency radio transmitter used as an instrument approach for airports and offshore platforms. | 190 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | AMAmplitude Modulation | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Phase Shift Keying (PSK) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying is a digital teletype mode based on Phase-Shift Keying (PSKPhase-Shift Keying) modulation. The most popular amateur radio PSKPhase-Shift Keying mode is PSKPhase-Shift Keying 31. | 1.838 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 909 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 10 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 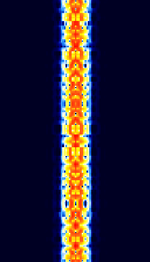 |
|
| Radio Teletype (RTTY) | RTTYRadio TeleTYpe (Also known as Baudot or ITA2) uses the Baudot 5-bit alphabet with FSKFrequency-Shift Keying to send text messages over the shortwave. This mode is gradually dying out in favor of more robust modes like PSK31 in the amateur service. | 147.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 28.15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 850 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Russian overhead power line telemetry system | Russian telemetry system, transmitted over the overhead power lines. | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 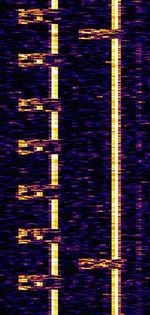 |
|
| SITOR-B | SITOR-B is one of two modes of SITOR (Simplex Teletype Over Radio). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 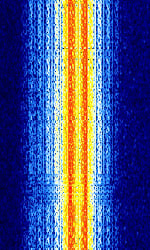 |
|
| Siemens CHX-200 FSK Modem | CHX200, also known as Siemens CHP200 and PRC-921/GY, is a backpack HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) ECCOM transceiver, designed and built by Siemens. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Single frequency russian overhead power line telemetry system | Russian telemetry system, transmitted over the overhead power lines. | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 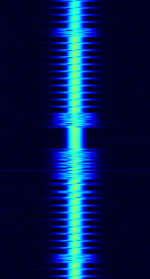 |
|
| Sonne | Sonne (Called Consol by the Britons) was a low-frequency radio range based radio navigation system used for long range navigation. | 250 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 350 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 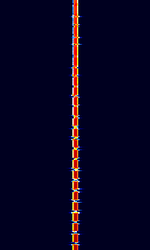 |
|
| Switching Electronic Interference | Commonly experienced interfering RFRadio Frequency emissions from switching electronics (i.e. switched-mode power supplies, power converters, digital electronics, etc.) which use inductors (coils) that unintentionally act as antennas. | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 200 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 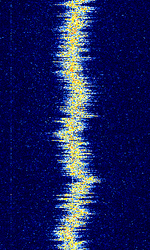 |
||||
| UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) Time Standard | UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) time standard transmission from NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) stations WWV in Fort Collins, Colorado USA (2.5, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz) and WWVH in Kauai, Hawaii (2.5, 5, 10, 15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz). | 2.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 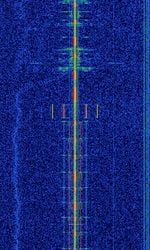 |
||
| WSPR | Weak Signal Propagation Reporter. | 136 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1,296.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 6 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 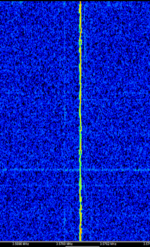 |
Pages in category "MF"
The following 42 pages are in this category, out of 42 total.