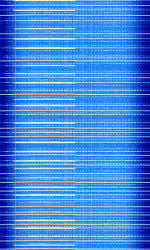
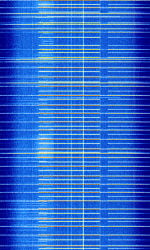
5G 'New Radio' Cellular Radio - Downlink
| Cellular | |
|---|---|
| 1G: AMPS - NMT 2G: GSM - D-AMPS - 2G CDMA (IS-95) |
 | |
|---|---|
| Frequencies | 600 MHz,50000 MHz,3600 MHz,700 MHz,850 MHz,900 MHz,2500 MHz,3700 MHz,28000 MHz,39000 MHz |
| Frequency Range | 600 MHz - 50000 MHz |
| Mode | CP-OFDM |
| Modulation | QPSK,16QAM,64QAM,256QAM |
| ACF | — |
| Emission Designator | — |
| Bandwidth | 100 MHz,5 MHz,10 MHz,15 MHz,20 MHz,25 MHz,30 MHz,40 MHz,50 MHz,60 MHz,70 MHz,80 MHz,90 MHz,200 MHz,400 MHz |
| Location | Worldwide |
| Short Description | 5G cellular, also known by 3GPP '5G' NR (new radio), etc. is a newly released cellular standard that allows for backwards compatibility with 4G LTE, and will allow for several gigabits of connection speeds, (up to 10-100Gb) per second. This is the 600 MHz downlink band for the new standard. |
| I/Q Raw Recording | Download file |
| Audio Sample | |
New Radio refers to the 5th generation of cellular technology (5G).
5G is currently in commercial use across more than 90 countries. In the U.S, AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile are the major 5G carriers.
T-Mobile launched commercial 5G service in 2019 with 600 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz (n71) and mmWave (n261, n260 and n258) bands. Merger with Sprint brought additional bands (n25, 1.9 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz and n41, 2.5 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz) for capacity.
5G can be either SA (Standalone) or non-Standalone (NSA) depending on the hardware and software implementations.
5G NR supports 2 distinct duplex modes, FDD and TDD. FDD, or Frequency Division Duplexing, utilizes paired spectrum with separate uplink and downlink channels. TDD, or Time Division Duplexing, allows both uplink and downlink to share the same spectrum by utilizing time slots. TDD bands such as n41, n77, and n78 are commonly used for high capacity deployments, while FDD is commonly used for coverage and stability.
NR Dual Connectivity (NR-DC) is a 5G connectivity option that allows simultaneous Sub6 and mmWave connections in NR SA deployments.
The actual sound of 5G is derived from 4G, its more of a "pulse sound", because of the UFMC modulation component.
Frequencies[edit]
There are 2 frequency ranges for 5G NR; Sub6 and mmWave (FR1 and FR2). The Sub6 range (FR1) is defined as any frequency below 6 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz, such as mid-band and low-band 5G service. FR1 allows channel bandwidths of 5 Mhz up to 100 Mhz. mmWave (FR2) refers to any frequency above 24 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz, which is known as millimeter wave spectrum. mmWave 5G often has much higher throughput compared to Sub6 due to the abundant spectrum which allows for aggregation up to 800mhz of bandwidth. FR2 allows channel bandwidths of 50 Mhz up to 400 Mhz.
List of frequencies can be found here.
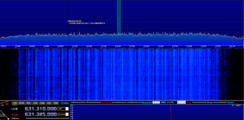
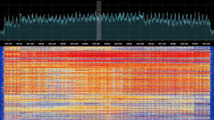
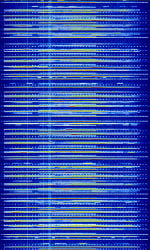
Additional Images[edit]
Samples[edit]
| 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz FR1 FDD Orange | 40 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz FR1 TDD Swan | 100 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz FR1 TDD Orange |
|---|---|---|
| IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis.: File:NR OR 10 downlink.zip | IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis.: File:NR 4ka 40 downlink.zip | IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis.: File:NR OR 100 downlink.zip |
FDD Mode[edit]
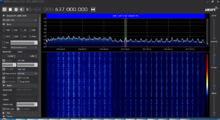
Dish Wireless band n71 (600 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz; Fujitsu Radios):
T-Mobile US band n71 (600 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz; Nokia Radios):
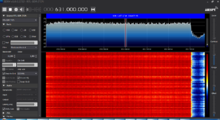
TDD Mode[edit]
T-Mobile US band n41 (2500 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz; Nokia Radios):