2G (GSM) Global System for Mobile Communications
| Cellular | |
|---|---|
| 1G: AMPS - NMT 2G: GSM - D-AMPS - 2G CDMA (IS-95) |
 | |
|---|---|
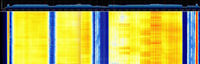
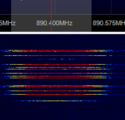
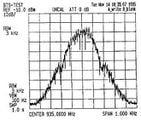
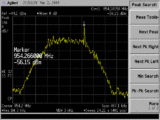
| Frequencies | 850 MHz,900 MHz,1800 MHz,1900 MHz |
| Frequency Range | 850 MHz - 1900 MHz |
| Mode | RAW, AM, FM |
| Modulation | GMSK |
| ACF | — |
| Emission Designator | — |
| Bandwidth | 200 kHz |
| Location | Worldwide |
| Short Description | GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standard developed by ETSI to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile phones. As of 2014, it has become the default global standard for mobile communications. |
| I/Q Raw Recording | Download file |
| Audio Sample | |
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications, originally Groupe Spécial Mobile), is a standard developed by ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile phones, first deployed in Finland in July 1991. As of 2014 it has become the default global standard for mobile communications - with over 90% market share, operating in over 219 countries and territories. As the need for more low-band 5G and 4G networks grow, operators around the world began phasing out GSM to re-farm spectrum. In the U.S, AT&T shut down GSM in 2017 while T-Mobile GSM continues to operate at reduced capacity in 2026. T-Mobile has begun shutting down its GSM network, however it is taking place slowly over the course of multiple years. In Australia, Optus GSM was decommissioned in 2017.
Samples[edit]
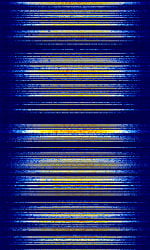
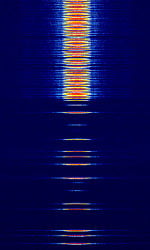
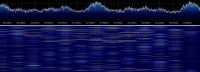
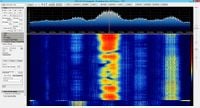
| Typical downlink broadcast channel | Typical downlink transport channel | Typical uplink - starting call |
|---|---|---|
| IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis.: File:GSM downlink BCCH.zip | IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis.: File:GSM TK 03 downlink TCH.zip |
- GSM Traffic Channels (TCHs)
GSM Non-Hopping Downlink, received with NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation:
GSM BCCH (Downlink); Non-Hopping, light traffic:
GSM Uplink; Non-Hopping, EDGE and calling:
GSM Hopping Uplink:
Frequencies[edit]
Info from Wikipedia page GSM Frequency Bands
| System | Band | Uplink (MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz) | Downlink (MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz) | Channel number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSM-850 | 850 | 824.2 – 849.2 | 869.2 – 893.8 | 128 – 251 |
| PCS-1900 | 1900 | 1850.2 – 1909.8 | 1930.2 – 1989.8 | 512 – 810 |
| E-GSM-900 | 900 | 880.0 – 915.0 | 925.0 – 960.0 | 975 – 1023, 0 - 124 |
| DCS-1800 | 1800 | 1710.2 – 1784.8 | 1805.2 – 1879.8 | 512 – 885 |
GSM-850 and PCS-1900 (shaded in blue) have been deployed in NAR and CALA (North American Region [Canada and the US], Caribbean and Latin America)
E-GSM-900 and DCS-1800 (shaded in yellow) have been deployed in EMEA and APAC (Europe, the Middle East and Africa, Asia-Pacific)
Decoding Software[edit]
- Hobby Level Software
- Professional Software
Decoding Tutorials[edit]
Video Examples[edit]
Additional Links[edit]
- ETSI GSM Part 1: General Description
- ETSI GSM Part 2: Logical Channels
- ETSI GSM Part 3: Modulation
- [http://goo.gl/mAu617 Tutorialspoint GSM - Specification