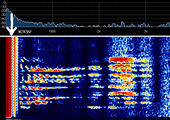
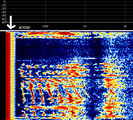
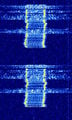
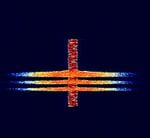
Digital-Coded Squelch (DCS)
 | |
|---|---|
| Frequencies | 433 MHz,446 MHz |
| Frequency Range | 433 MHz - 446 MHz |
| Mode | NFM |
| Modulation | FSK |
| ACF | — |
| Emission Designator | — |
| Location | Worldwide |
| Short Description | Digital in-band signalling used to squelch and manage transmissions on a given frequency. |
| I/Q Raw Recording | Download file |
| Audio Sample | |
Digital-Coded Squelch (DCS), generically known as Continuous Digital-Coded Squelch System (CDCSS), was designed as the digital replacement for CTCSS. In the same way that a single CTCSS tone would be used on an entire group of radios, the same DCS code is used in a group of radios. DCS is also referred to as Digital Private Line (or DPL), another trademark of Motorola, and likewise, General Electric's implementation of DCS is referred to as Digital Channel Guard (or DCG). DCS is also called Digital Tone Code Squelch (DTCS) by Icom, and other names by other manufacturers. Radios with DCS options are generally compatible, provided the radio's encoder-decoder will use the same code as radios in the existing system.
DCS adds a 134.4 bpsBits per second (bps) (sub-audible) bitstream to the transmitted audio. The code word is a 23-bit Golay (23,12) code which has the ability to detect and correct errors of 3 or fewer bits. The word consists of 12 data bits followed by 11 check bits. The last 3 data bits are a fixed '001', this leaves 9 code bits (512 possibilities) which are conventionally represented as a 3-digit octal number. Note that the first bit transmitted is the LSBLower Side Band Modulation, so the code is "backwards" from the transmitted bit order. Only 83 of the 512 possible codes are available, to prevent falsing due to alignment collisions.
Samples[edit]
Sound from USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)