Very Low Frequency (VLF)
From Signal Identification Wiki
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) encompasses frequencies from 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz to 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | Beta is the designation of a time signal service which is transmitted from multiple Russian VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) stations. | 20.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | CWContinuous Wave, OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, Worldwide | 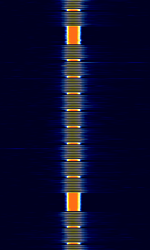 |
|
| Grimeton Radio (SAQ) | SAQ stands as the sole transmitter reliant on an alternating current generator. Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site, it employs the last operational Alexanderson alternator for RFRadio Frequency production. | 17.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | Sweden | 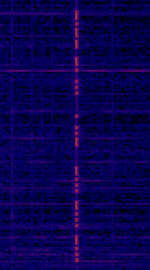 |
|||
| ICV | ICV is a NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization-operated VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) transmitted located in the island of Tavolara, Sardinia, Italy. | 20.27 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 20.76 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Italy | 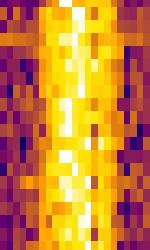 |
||
| Induction cooker interference | RFRadio Frequency interference from nearby induction cooker can sometimes be mistaken for a real LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) or VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) transmission. | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | Worldwide | 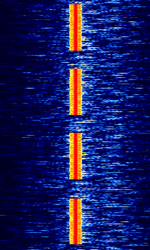 |
|||
| Jim Creek (NLK) | Jim Creek Naval Radio Station is used by the US Navy to transmit commands to distant submarines. | 24.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 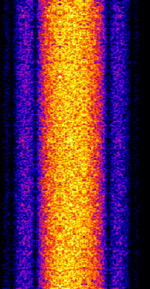 |
|
| Lightning Sferics | VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) RFRadio Frequency emissions from lightning in the atmosphere that can affect up to HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) frequencies and beyond depending on strength. Has a popping crackle sound with both USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) and AMAmplitude Modulation modes of reception. | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 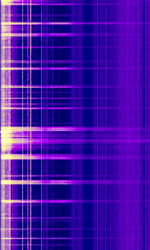 |
||||
| NML | Naval Radio Transmitter Facility (NRTF) transmits encrypted commands to submerged US submarines. | 25.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 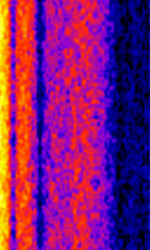 |
|
| NOV | TACAMO (take charge and move out) is the back up communications system to the US nuclear submarine fleet in case an attack on land based transmitters disables them. A rotating fleet of Navy E6 jets equipped with 200 KW transmitters and two 2½-mile-long trailing wire antennas (TWA) at 35,000 ft altitude to provide 24/7 coverage. Short pings are transmitted every few seconds. | 26.9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | Worldwide | 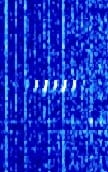 |
|||
| NPM | Naval Radio Transmitting Facility (NRTF) sends encrypted commands to submerged US naval submarines in the Pacific. | 21.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 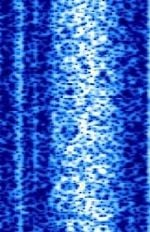 |
|
| NWC | Naval Communication Station (NCS) Harold E. Holt. Used jointly by the Australian and United States navies to transmit encrypted orders to submerged submarines in the Pacific. | 19.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Australia | 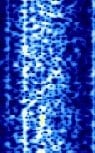 |
|
| RDL VLF | RDL is a Russian VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) station located in Krasnodar. It is one of the few VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) stations that changes modes during routine transmissions. | 18.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 27.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, CWContinuous Wave-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 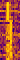 |
|
| Radioteknicheskaya Systema Dalney Navigatsii (RSDN-20) | RSDN-20, also known as Alpha, is a Russian hyperbolic radio navigation system. Presumed to be used for Russian ships, submarines and aircraft in the northern hemisphere, possibly worldwide. | 11.91 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 14.88 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | 20 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia |  |
||
| Switching Electronic Interference | Commonly experienced interfering RFRadio Frequency emissions from switching electronics (i.e. switched-mode power supplies, power converters, digital electronics, etc.) which use inductors (coils) that unintentionally act as antennas. | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 200 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 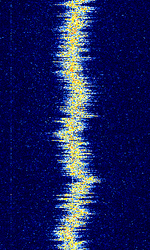 |
Pages in category "VLF"
The following 15 pages are in this category, out of 15 total.