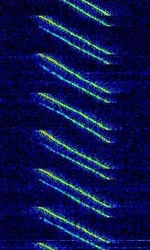
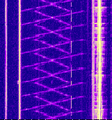
CODAR
CODAR (Coastal Ocean Dynamics Applications Radar) is used for near-surface ocean monitoring, such as waves and water current. Commonly becomes a source of interference for amateur radio operators. Developed between 1973 and 1983 at NOAA's Wave Propagation Laboratory, the founders left NOAA and formed the CODAR Ocean Sensors company, producing CODAR radar systems for commercial use.
CODAR is based on Bragg’s Scattering Law. This allowed for the monitoring of ocean current and wave condition with high precision and range of up to 200 km. CODAR uses ILFM (Interpulse Linear Frequency Modulation), which is essentially a FMCW signal that is broken up into pulses in order to create a 50% duty cycle.
Frequencies[edit]
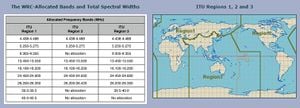
CODAR can operate on frequencies between 4.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz and 50 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz.
Chart valid as of 2012.
Video Examples[edit]
- Radar, CODAR, 4435 kHz cf, Ocotober 10, 2010, 1720 UTC
- Radar, CODAR x2, 4550 kHz cf, March 08, 2009, 0822 UTC
- Radar, CODAR in 20M ham band, May 27, 2012, 1436 UTC
- CODAR Radar at 4.785 MHZ
Additional Links[edit]
- Wikipedia CODAR
- CODAR Ocean Sensors
- Southern California Coastal Ocean Observing System, CODAR Realtime Data Plot, Californian Coast
- CODAR SeaSonde Information
- ITU Guidelines for the use of spectrum by oceanographic radars
Additional Images[edit]
|
|